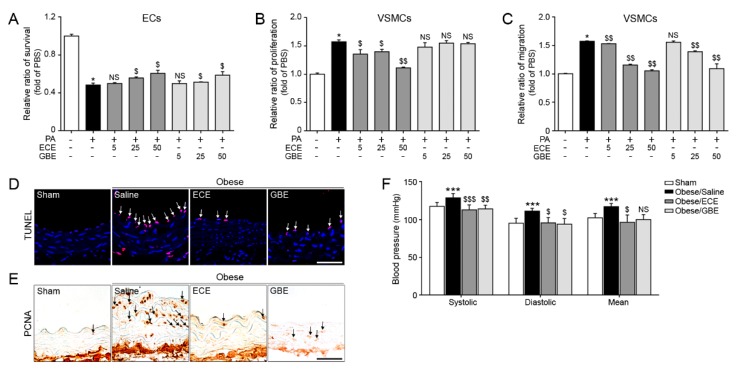
Figure 1.
Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract (GBE) and Ecklonia cava extract (ECE) on vascular dysfunction in vitro and in vivo (A) endothelial cells (ECs) (SVEC4-10; mouse endothelial cells) were exposed to Palmitate/Phosphate-buffered saline (PA/PBS), Palmitate/ECE (PA/ECE) or Palmitate/GBE (PA/GBE). The survival ratios of ECs were measured using a cell survival assay. (B,C) PA/PBS, PA/ECE, or PA/GBE were administered to vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) (MOVAS, mouse vascular smooth muscle cells), and proliferating to migrating VSMC ratios were measured by respective assays. (D) Confocal microscopic images showing apoptotic cells as TUNEL positive cells (red, arrows) and DAPI stained nuclei (blue). Scale bar = 50 μm (E) Light microscopic images showing proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) positive cells (brown, arrow) in obese mice. Scale bar = 10 μm (F) Blood pressure plots of systolic, diastolic, and mean artery blood pressure in obese mice. *, P < 0.05 and ***, P < 0.001 vs. the PBS (Sham) group; $, P < 0.05, $$, P < 0.01 and $$$, P < 0.001 vs. PA (or DIO/Saline) group; NS, not significant. Results are presented as means ± SD. ECE, E. cava extract; GBE, leaf of GB extract; PCNA, Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; TUNEL, Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling.