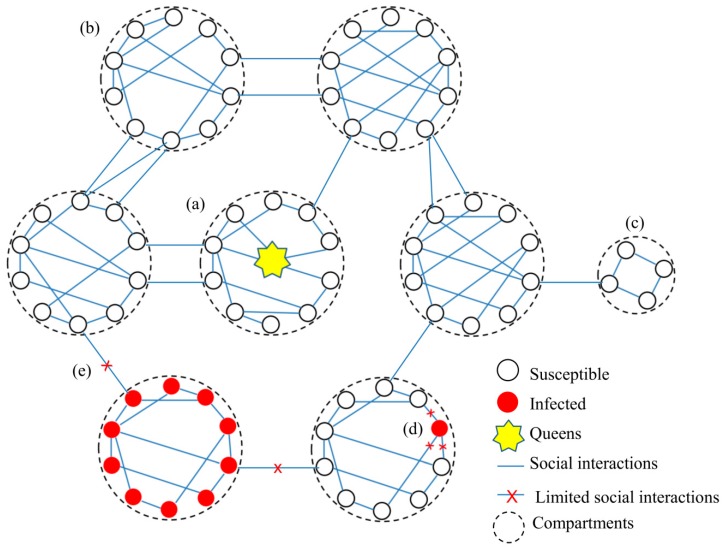
Figure 2.
Organizational immunity in a generalized social insect colony. (a) The compartments consisting of queens and her broods are specially cared in the central area; (b) the compartments consisting of older workers serve protections in the periphery to prevent environmental pathogens from entrance into the central area; (c) the compartments consisting garbage and dead bodies are far away from and are stopped from direct interaction with the central area to protect queens from pollutions. In addition, the social interaction occurs more frequently within compartments than between compartments. When (d) individuals were infected, the social interactions between the infected and naïve individuals were limited within compartments. However, when (e) compartments were infected, the rest of the compartments would close the entrance and hence cutoff the interaction between the infected and naïve compartments. These managements are effective to limit the pathogens transmission and protect high-value individuals in social insect colonies.