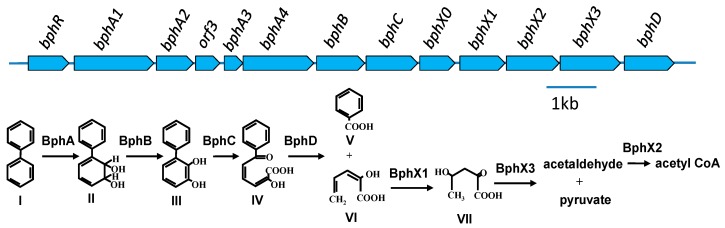
Figure 1.
Catabolic pathway of the biphenyl degradation and organization of the bph gene cluster in P. furukawaii KF707. Compounds: I, biphenyl; II, 2,3-dihydroxy-4-phenylhexa-4,6-diene (dihydrodiol compound); III, 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl; IV, 2-hydroxy-6-oxo-6-phenylhexa-2,4-dienoic acid (biphenyl meta-cleavage compound: HOPD); V, benzoic acid; VI, 2-hydroxypenta-2,4-dienoic acid; VII, 4-hydroxy-2-oxovalerate. Enzymes: BphA1-BphA2-BphA3-BphA4, biphenyl dioxygenase; BphB, dihydrodiol dehydrogenase; BphC, 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl dioxygenase; BphX0, glutathione S-transferase; BphX1, 2-hydroxypenta-2,4-dienoate hydratase; BphX2, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (acylating); BphX3, 4-hydoxy-2-oxovalerate aldolase; BphD, 2-hydroxy-6-oxo-6-phenylhexa-2,4-dieonic acid hydrolase. The BphR protein, belonging to the GntR family, is a transcriptional regulator involved in the expression of bphR and bphX0X1X2X3D. The function of orf3 remains unclear.