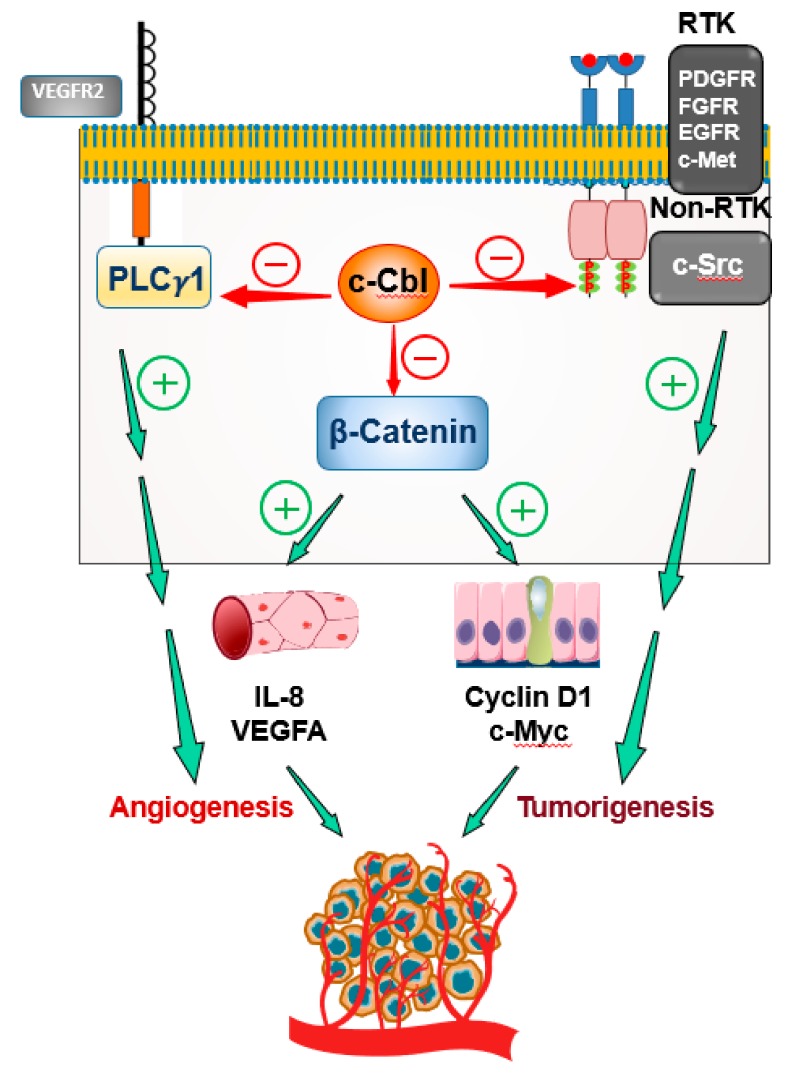
Figure 3.
c-Cbl is an attractive therapeutic target for angiogenesis and tumorigenesis. In the endothelial cells of vessels supplying the tumor, Wnt activation results in secretion of pro-angiogenic cytokines IL-8 and VEGF-A that augment tumor-induced angiogenesis. In colon cancer epithelial cells, inactivating mutations in APC tumor suppressor stabilizes β-Catenin and allows its nuclear translocation. This event results in the transcription of pro-proliferative and pro-oncogenic genes such as Cylin D1 and c-Myc to augment oncogenic activity. c-Cbl, by ubiquitinating nuclear β-Catenin in endothelial cells and in colon cancer cells, suppresses the growth of blood vessles and tumors. In addition, c-Cbl suppresses these processes by downregulating other pathways such VEGF signaling (PLCγ1) and mitogenic signaling (RTK and non-RTKs).