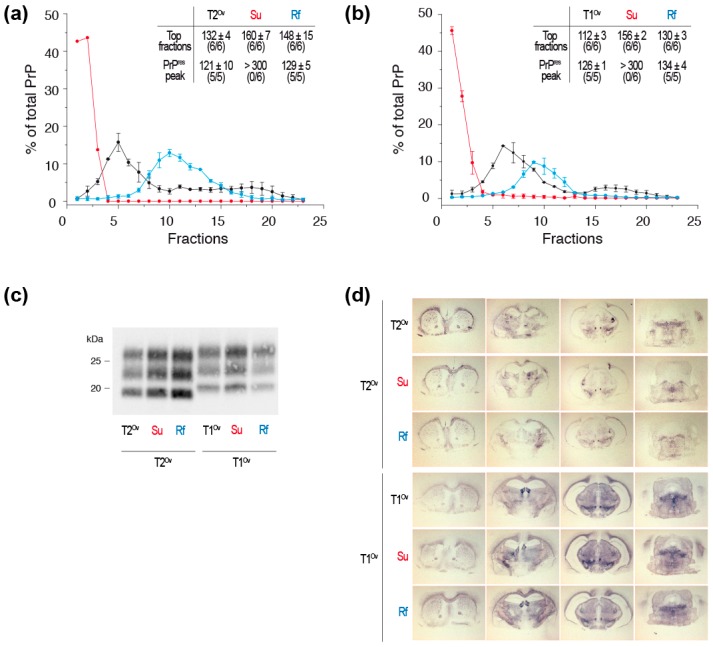
Figure 3.
Infectivity and strain properties of suPrPU and rfPrP from T1Ov and T2Ov prions. Tg338 brains homogenates were treated with 6M urea and either directly SV-fractionated to isolate suPrPU oligomers or dialyzed before SV-fractionation to isolate rfPrP assemblies. The resulting fractions corresponding to suPrPU and rfPrP were inoculated to groups of reporter tg338 mice (same method as in [53]). (a) Sedimentograms of untreated T2Ov prions (black line), 6M urea treated T2Ov prions (red line, suPrPU) and 6M urea-treated and dialyzed T2Ov prions (blue line, rfPrP) (data from [53]) and as insert, incubation times of the mice inoculated with the top fractions (fractions 1–3) and the PK-resistant PrPSc (PrPres) peak (fractions 5–7 for untreated T2Ov, fractions 10–12 for suPrPU and rfPrP). (b) Sedimentograms of untreated T1Ov prions, 6M urea treated T1Ov prions (suPrPU) and 6M urea-treated and dialyzed T1Ov prions (rfPrP) (data from [53]) and as insert, incubation times of the mice inoculated with the top fractions (fractions 1–3) and the PrPres peak (fractions 5–7 for untreated T1Ov, fractions 8–10 for suPrPU and rfPrP). (c) PrPres electrophoretic pattern and (d) PrPres neuroanatomical deposition (histoblots) in the brains of tg338 mice inoculated with the top fractions and the PrPres peak fractions from untreated T2Ov and T1Ov prions, 6M urea treated T2Ov and T1Ov prions (suPrPU) and 6M urea-treated and dialyzed T2Ov and T1Ov prions (rfPrP). The western blot and histoblot methods used here have been comprehensively described in [8,23,25,53].