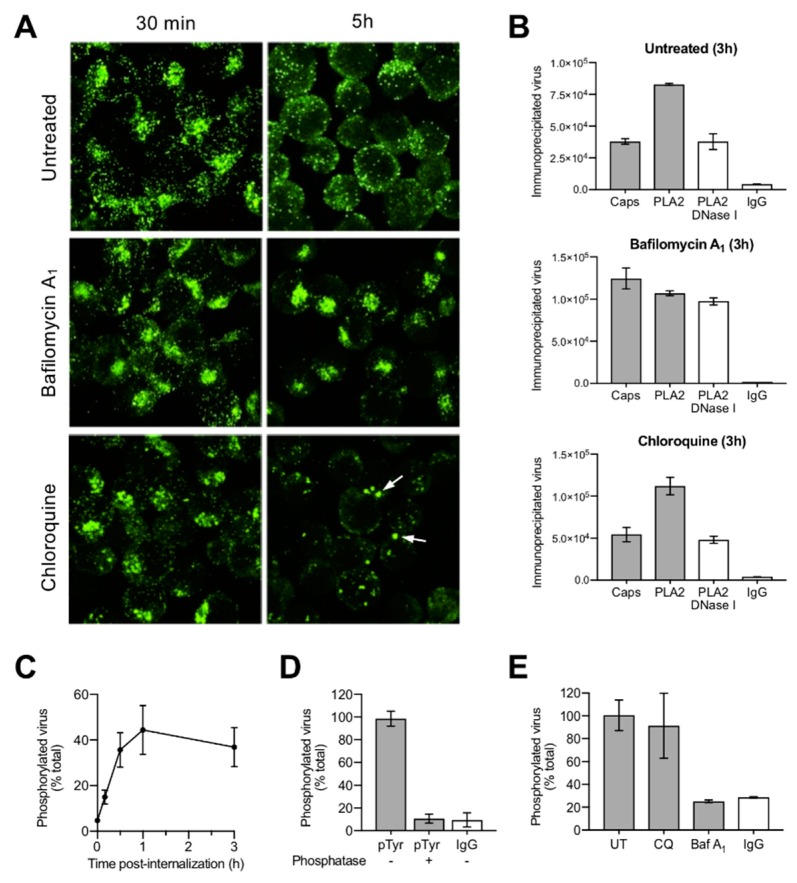
Figure 5.
Conformational epitope rearrangement, DNA externalization and phosphorylation occur after endosomal escape. (A) Effect of BafA1 and CQ on endosomal escape and conformational epitope integrity. Immunofluorescence images of infected cells treated or not with BafA1 (20 nM) and CQ (25 µM). The integrity of the conformational epitope and the characteristic endocytic clustering of the virus was examined by staining with the conformational antibody (Caps) at 30 min and 3 h pi. Arrows indicate the presence of enlarged endosomes in cells treated with CQ. (B) Effect of BafA1 and CQ on the conformational rearrangement and nuclease sensitivity of the incoming virions. The virions were immunoprecipitated from infected cells at 3 h pi and quantified by qPCR, values correspond to geq/µL. (C) Kinetics of B19V phosphorylation. At increasing times pi, virions were immunoprecipitated from cytoplasmic fractions with PLA2 (total virions) or with an antibody against phosphotyrosine and quantified by qPCR. (D) Phosphatase treatment abrogated the reactivity with the phosphospecific antibody. Before immunoprecipitation, the intracellular capsids were treated or not with lambda phosphatase (500 U) for 1 h at 30 °C. (E) Effect of BafA1 (20 nM) or CQ (25 µM) on B19V phosphorylation. Virions from cytoplasmic fractions were immunoprecipitated with the phosphotyrosine antibody at 3h pi and quantified by qPCR. As control, an unrelated IgG was used.