Figure 1.
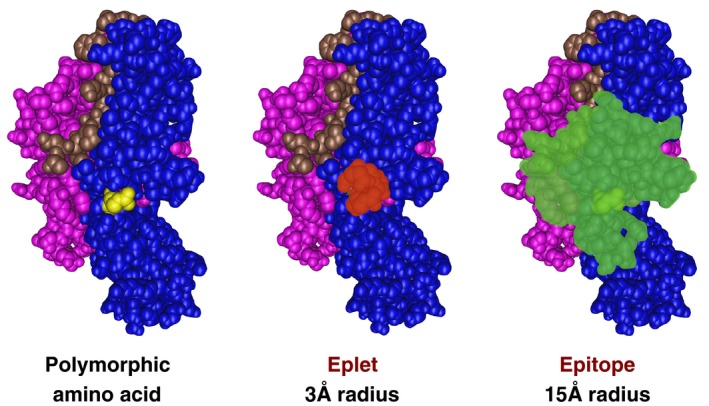
HLA donor‐recipient mismatch drives allorecognition. An amino acid polymorphism (yellow) present in the donor and not present in the recipient is the most basic unit of mismatch. An eplet is defined as a single polymorphic amino acid or a small patch of polymorphic amino acids within a 3 angstrom (0.3 nm) radius on or near the surface of an HLA molecule. An eplet represents the smallest functional unit of an epitope‐paratope interface, which may drive antibody specificity through interactions with the central complementary determining regions of the antibody paratope. The complete epitope (green) represents all amino acids within a 15 angstrom (1.5 nm) radius typical for an antibody paratope
