Table 1.
Biotransformations with 2‐ODD‐PH.
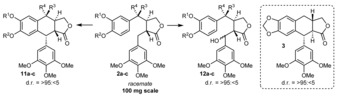
| Entry | Substrate | HPLC area | Yield | ee of | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1= | R3= | [%][a] | [%][b] | 2 a–c | ||||
| R2= | R4= | 11 a–c | 12 a–c | 11 a–c | 12 a–c | [%][c] | ||
| 1 | rac‐2 a | ‐CH2‐ | H H |
27[d] | – | 19[e] | – | 10 |
| 2[f] | rac‐2 b | ‐CH2‐ | H OH |
– | 29 | – | 15 | 46 |
| 3 | rac‐2 c | Me Me |
OH H |
12 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 26 |
Reaction conditions: Cell‐free extract (CFE, 44 v %), 20 mm substrate, 2‐oxoglutarate (1.75 equiv), sodium ascorbate (3 equiv), 23 % DMSO as cosolvent. [a] Determined by peak area integration of the HPLC‐UV chromatogram (at 215 nm). [b] Yields of isolated, chromatographically pure, and fully characterized products are reported; [c] ee was determined via HPLC‐UV on a chiral stationary phase (for details see the Supporting Information). [d] With 37 % of diastereoisomer 3. [e] 20 % of compound 3 were isolated from the same batch; [α]D 20 values for 11 a and 3 are in full consistency with literature values.24 [f] The experiment was conducted on 50 mg substrate scale. Bold and dashed lines refer to relative stereochemistry; bold and dashed wedges refer to absolute stereochemistry.
