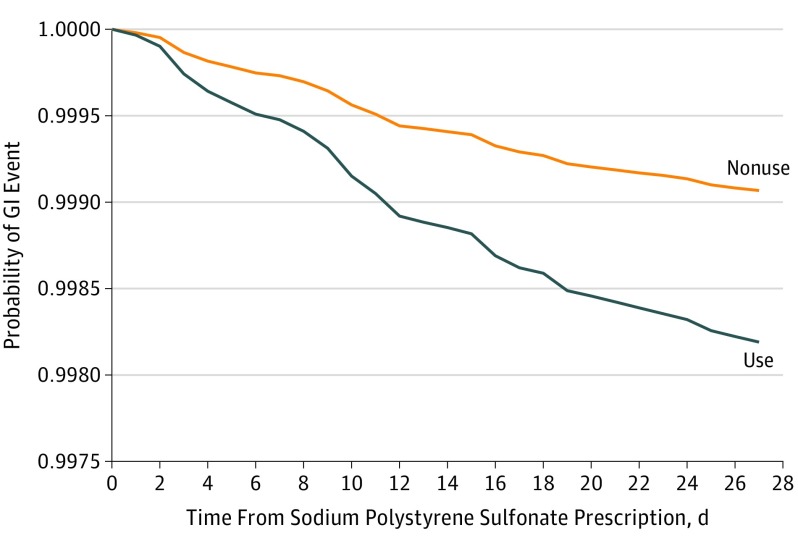
Figure. 30-Day Probability of Gastrointestinal (GI) Injury Requiring Hospitalization or Emergency Department Visit Associated With Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate Use Compared With Nonuse.
Results presented are for the matched analysis of sodium polystyrene sulfonate users to nonusers on the logit of the high-dimensional propensity score (±0.2 of the standard deviation) and the following: age, sex, diabetes, congestive heart failure, prior acute kidney injury, chronic dialysis, history of hyperkalemia, previous nephrologist visit, medication use (β-blocker or renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade), and index date (within 1 year). Additional adjustment was for place of residence.