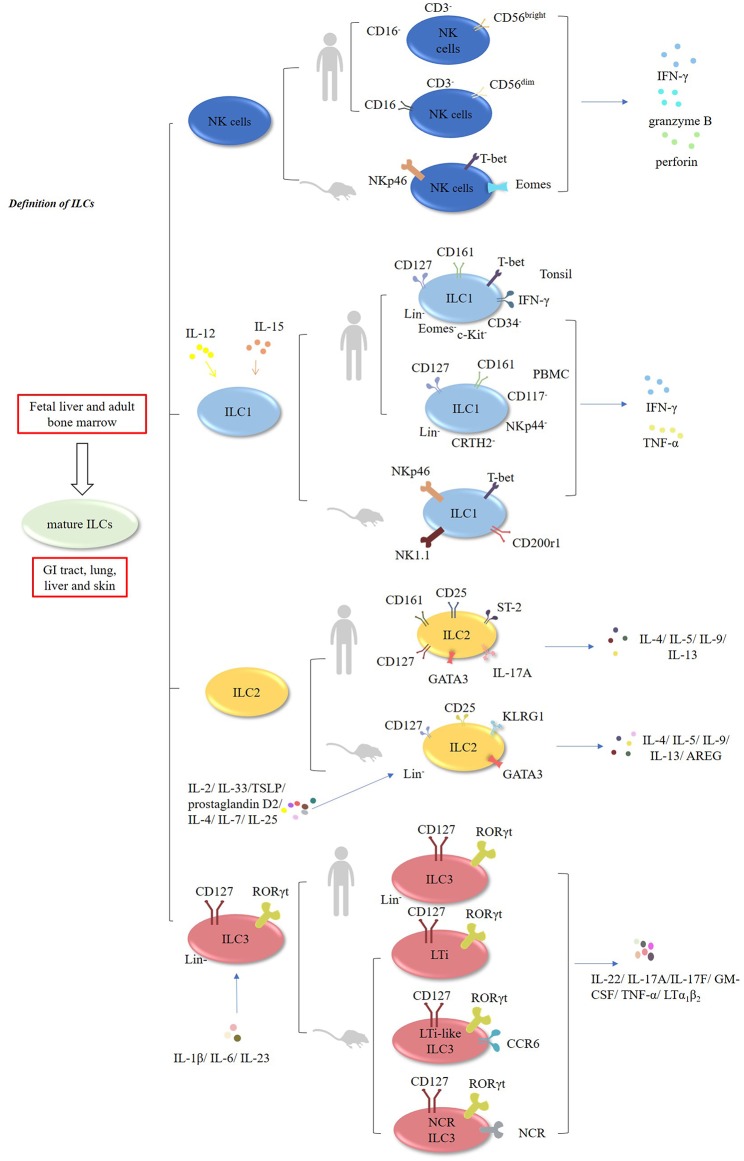
Figure 1.
Characteristic of ILCs. ILCs encompass NK, ILC1, ILC2, and ILC3 cells. Murine and human NK cells can secrete IFN-γ, granzyme B, and perforin. In humans, NK cells have two main subsets: CD3−CD56brightCD16− and CD3−CD56dimCD16+ cells. ILC1 cells can respond to IL-12 and IL-15, and subsequently produce IFN-γ and TNF-α. In humans, CD127+CD161+ CD34− c-Kit−T-bet+ Eomes− IFN-γ+ ILC1 cells are enriched in the tonsils. Additionally, Lin−CD127+CD161+ CD117− NKp44−CRTH2− ILC1 cells have been found in the human PBMCs. In mice, ILC2 cells are Lin−CD127+CD25+ KLRG1+ GATA3high cells which are responsive to IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-25, IL-33, TSLP, and prostaglandin D2, and subsequently produce multiple effector cytokines. In humans, ILC2 cells express GATA3, CD127, CD161, CD25, ST-2, IL-17A, and CRTH2. Both murine and human ILC3 cells are Lin−CD127+RORγt+. They are responsive to IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-23, and produce IL-22, IL-17A, IL-17F, GM-CSF, TNF-α, and LTα1β2.