Figure 2.
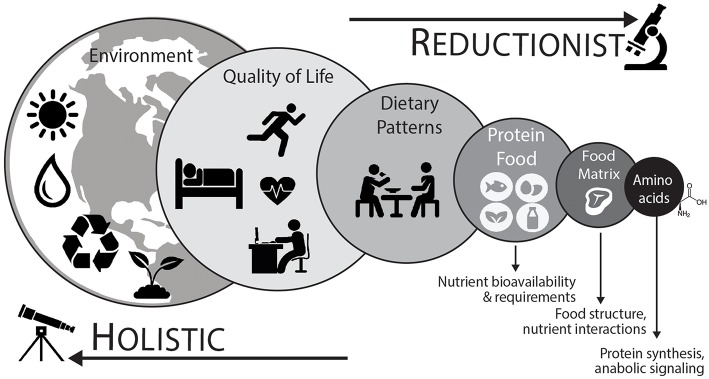
To adequately define optimal protein intakes it is important to consider an integrative holistic approach. This “top-down” approach considers that different levels are additive to the next for the development of dietary advice (110, 111). Dietary patterns (animal based vs. plant based) and their associated protein foods are directly connected. Protein food is more than the sum of its constituent amino acids and the net effect of the food matrix, or food combinations (e.g., complementary protein pairing of plant-based foods), likely has an impact on the stimulation of postprandial muscle protein synthetic responses and overall diet quality. At the highest levels, food sustainability, food waste, and other human choices are important considerations. At the lowest (reductionist) level, amino acids represent the fundamental building blocks of protein and are anabolic agents in themselves (i.e., initiate protein synthesis). Aside from nutrient factors, ample physical activity, including regular structured exercise, is important component of a healthy lifestyle and has a direct impact on protein utilization and the overall nutritional recommendation.