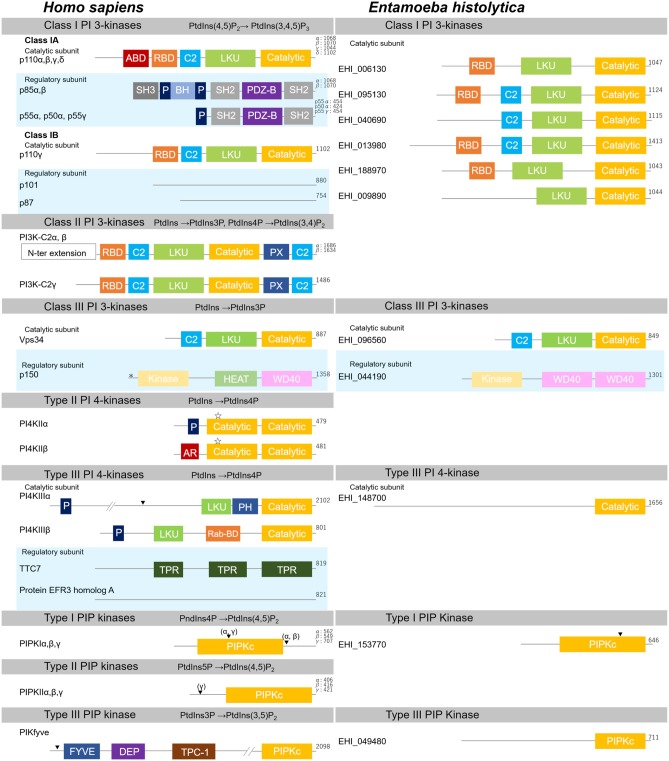
Figure 3.
Structural features of PI kinases of H. sapiens and E. histolytica. Structural features and domain organization of PI kinases, including their regulatory subunits are shown. Numbers showing at the end of the protein indicates amino acid length. ABD, adaptor binding domain; AR, acidic region; BH, Bcl Homology; C2,C2 domain; Catalytic, lipid kinase domain of PI 3- and PI 4-kinases; DEP, disheveled, Egl-10 and pleckstrin domain; FYVE, Fab1, YOTB, Vac1, and EEA1 domain; HEAT, Huntington, Elongation factor3, PR65/A, and TOR; Kinase, Ser/Thr kinase domain; LKU, lipid kinase unique domain; P, Proline-rich; PDZ-B, PDZ domain binding domain; PH, Pleckstrin-homology; PIPKc, kinase core domain of PIP kinases; PX, Phox homology; Rab-BD, Rab binding domain; RBD, Ras binding domain; SH2, Src homology 2; SH3, Src homology 3; TPC-1, T-complex 1 homology; TPR, tetratricopeptide repeat; WD40, WD40 repeat. Myristoylation, palmitoylation sites, and the nuclear localization signal are also depicted with “*”, “ ”, or “▾”, respectively.
”, or “▾”, respectively.