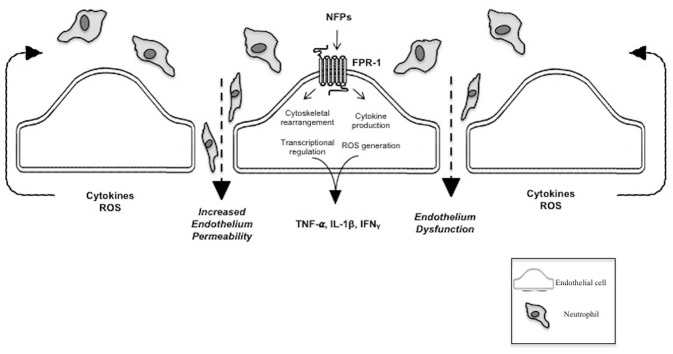
Figure 1.
N-Formyl peptide mediated pathophysiology of SIRS and sepsis. This figure shows the pathogenic effect of NFPs on the vascular endothelium via FPR-1 activation. FPR-1 activation results in dysfunction of the vascular barrier allowing infiltration of immune cells and molecules into the interstitial and extravascular space. NFPs, bacterial and mitochondrial N-Formyl peptides; FPR-1, formyl peptide receptor-1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; ILF-1β, interleukin-1 beta; IFNγ, Interferon gamma; ROS, reactive oxygen species.