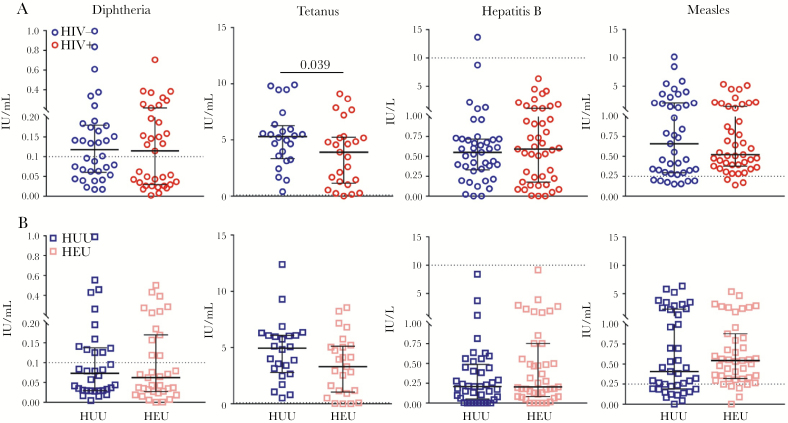
Figure 3.
Vaccine-specific antibody levels in HIV- vs HIV+ mothers and HIV-unexposed uninfected (HUU) vs HIV-exposed but uninfected (HEU) neonates. A, Maternal antibody concentrations (circles) in HIV- (blue) and HIV+ (red) mothers. B, Corresponding neonatal antibody concentrations (squares) in HUU (navy blue) and HEU (pink) neonates. From left to right: diphtheria (n = 34 HIV-/HUU, n = 35 HIV+/HEU), tetanus (n = 24 HIV-/HUU, n = 25 HIV+/HEU), hepatitis B (n = 41 HIV-/HUU, n = 43 HIV+/HEU), and measles (n = 41 HIV-/HUU, n = 43 HIV+/HEU). Horizontal dotted lines represent antibody concentrations considered to be protective against infection (diphtheria, 0.1 IU/mL; tetanus, 0.1 IU/mL; hepatitis B, 10 IU/L; and measles, 0.25 IU/mL) All data points are plotted, and medians with interquartile ranges are superimposed. Medians were compared for each antibody using the Mann-Whitney test. P values are presented for statistically significant differences.