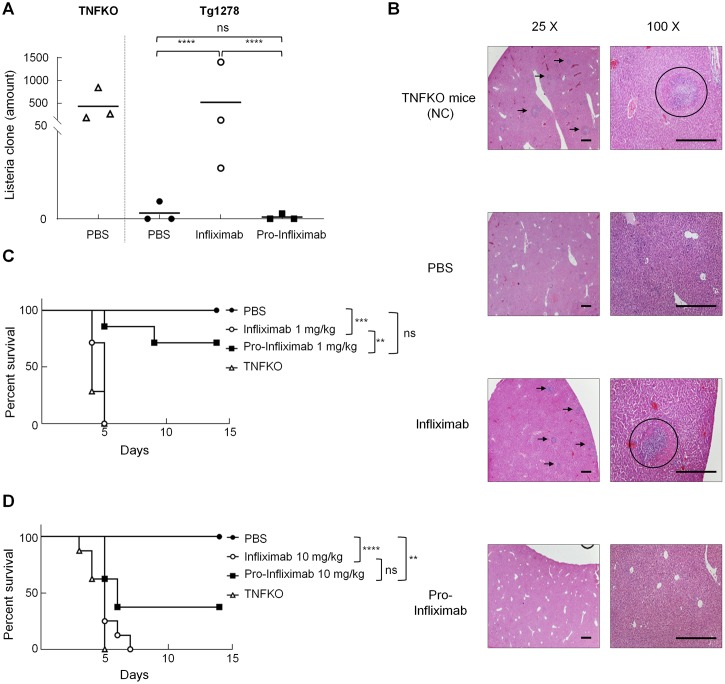
Fig 6. Comparison of the protective ability between pro-Infliximab and Infliximab on the host defense of TNFKO and Tg1278 TNFKO mice against Listeria infection.
The Tg1278 mice (n = 3) were intraperitoneally injected with 1 and 10 mg/kg of pro-Infliximab, Infliximab, or control saline and challenged with lethal dosage of L. monocytogenes (×104 CFU) 2 h later. The blood CFU counts (A) and representative HE staining (B) of liver tissues were tested to compare the host defense of Listeria infection. The arrows and circles represent the sites of infection identified as big well-shaped granuloma structures containing necrotic hepatocytes and inflammatory cells. Bars = 500 μm. (C and D) Survival rate after PBS, Infliximab. or pro-Infliximab treatment at low dose (1 mg/kg) (C) and high dose (10 mg/kg) (D) in L. monocytogenes-infected mice. The values are mean ± SEM and the asterisks indicate a significant difference, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P< 0.0001. Error bar: standard error of triplicate determinations. Underlying data can be found in S1 Data. CFU, colony-forming unit; HE, hematoxylin–eosin; NS, no significance; Tg1278 mice, hTNFα-transgenic mice; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; TNFKO, TNFα knockout.