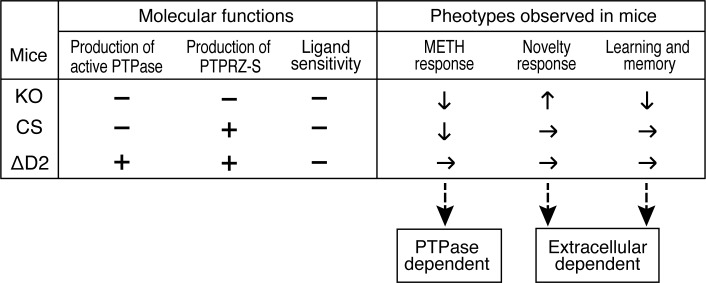
Fig 7. Summary of Ptprz-KO, and Ptprz-CS and ΔD2 knock-in mutant mouse phenotypes.
Molecular function is maintained (+) or disrupted (–). The phenotype is evident (Up/increase or down/decrease with arrows) or not (horizontal arrows). Ligand (PTN) sensitivity means the ligand-induced PTPase inactivation of PTPRZ receptors. Distinct physiological roles of PTPRZ isoforms might be a reason to explain the discrepancy in the myelination phenotype between our Ptprz-KO mice [7, 8, 29] and another KO mouse line [13], which is mentioned in the introduction section. Because the latter KO line was generated by the replacement of an exon encoding a portion of the extracellular CAH domain with a pgk-neo cassette [5], which may result in unexpected expression of an aberrant extracellular fragment of PTPRZ.