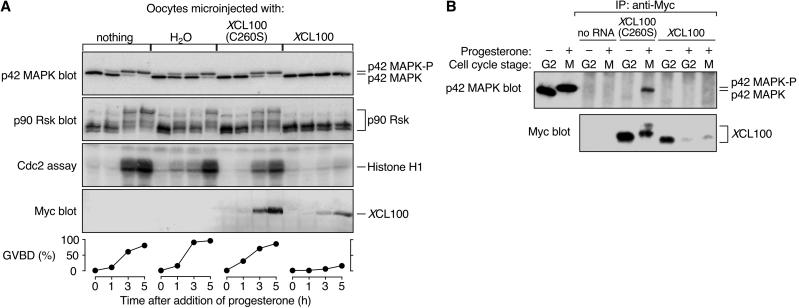
Figure 1.
XCL100 functions as a p42 MAPK phosphatase in oocytes. (A) Overexpressed XCL100 prevents progesterone-induced meiotic maturation. Stage VI oocytes were microinjected with either water or mRNA (50 ng) encoding Myc-tagged XCL100 or XCL100(C260S), and incubated briefly to initiate protein expression. GVBD and activation of p42 MAPK, p90 Rsk, and Cdc2 were monitored at various times after the addition of progesterone (5 μg/ml). Activation of p42 MAPK and p90 Rsk was assessed by immunoblotting, Cdc2 activation was assessed by histone H1-directed kinase activity in p13 Suc1-agarose precipitates, and GVBD was scored by the appearance of a white spot at the animal pole of the oocyte. Expression of Myc-tagged XCL100 proteins was assessed by immunoblotting with the Myc antibody 9E10. (B) XCL100(C260S) forms a stable complex with active p42 MAPK in vivo. G2- and M-phase oocytes (10 per sample) expressing XCL100 or XCL100(C260S) were lysed and subjected to immunoprecipitation with 9E10. Half of each sample was immunoblotted with the p42 MAPK antiserum DC3, and the other half was immunoblotted with 9E10 to detect XCL100 proteins. The first two lanes of the p42 MAPK blot represent uninjected oocytes (one per lane) incubated with (+) or without (−) 5 μg/ml progesterone as controls for active and inactive p42 MAPK, respectively. Cell cycle stage was determined by the presence (M) or absence (G2) of GVBD. p42 MAPK-P, phosphorylated, active p42 MAPK.