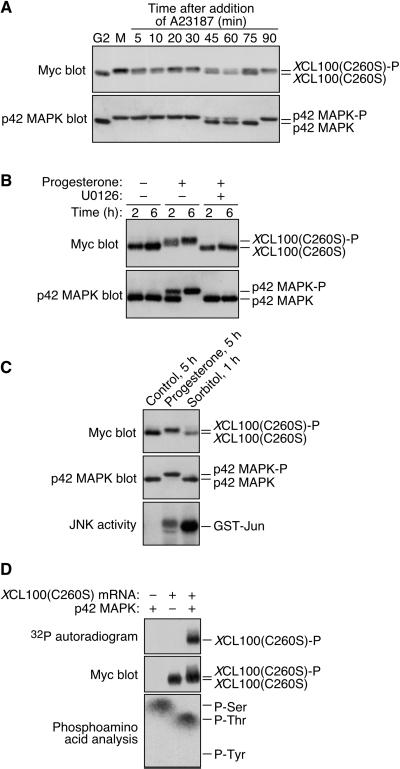
Figure 3.
M-phase phosphorylation of XCL100(C260S) is p42 MAPK dependent. (A) XCL100(C260S) phosphorylation parallels that of p42 MAPK throughout meiosis. Stage VI oocytes were microinjected with mRNA (41 ng) encoding Myc-tagged XCL100(C260S) and incubated overnight in the presence or absence of 5 μg/ml progesterone. The next day, immature (G2) oocytes were collected immediately; mature oocytes (M) were transferred to OR2 containing 5 μM A23187, and collected at the indicated times. XCL100(C260S) was detected by 9E10 immunoblotting, after which blots were stripped and reprobed with DC3 to detect p42 MAPK. (B) Inhibition of MEK prevents progesterone-induced XCL100(C260S) phosphorylation. Stage VI oocytes expressing XCL100(C260S) were pretreated for 2 h with 50 μM U0126 or an equal volume of dimethyl sulfoxide (0.5%) as a control. Oocytes were then left unstimulated (−) or stimulated with (+) 5 μg/ml progesterone, and samples were collected at the indicated times after progesterone treatment (GVBD50 of ∼2.5 h). XCL100(C260S) was detected by 9E10 immunoblotting, and p42 MAPK was detected by DC3 immunoblotting. U0126 completely blocked progesterone-induced GVBD in this experiment. (C) Hyperosmolar stress neither activates p42 MAPK nor brings about XCL100(C260S) phosphorylation. Stage VI oocytes expressing XCL100(C260S) were left unstimulated for 5 h, stimulated with 5 μg/ml progesterone for 5 h (GVBD50 of ∼3.5 h), or treated with 0.2 M sorbitol for 1 h. XCL100(C260S) and p42 MAPK were detected by immunoblotting with 9E10 (top) and DC3 (middle), respectively. JNK activity assays (five oocytes per sample) were performed as described (Bagowski et al., 2001), and phosphorylated GST-Jun was visualized by autoradiography (bottom). (D) p42 MAPK phosphorylates XCL100(C260S) on serine and threonine in vitro. Lysates from G2-arrested oocytes expressing XCL100(C260S) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with 9E10. Immunoprecipitates were treated with (+) or without (−) active mouse p42 MAPK (2 U/μl) plus [γ-32P]ATP for 30 min at 30°C and analyzed by autoradiography (top) and 9E10 immunoblotting (middle). Phosphoamino acid analysis of phosphorylated XCL100(C260S) (bottom) was performed as described in Figure 2D. XCL100(C260S)-P, phosphorylated XCL100(C260S).