Fig. 5.
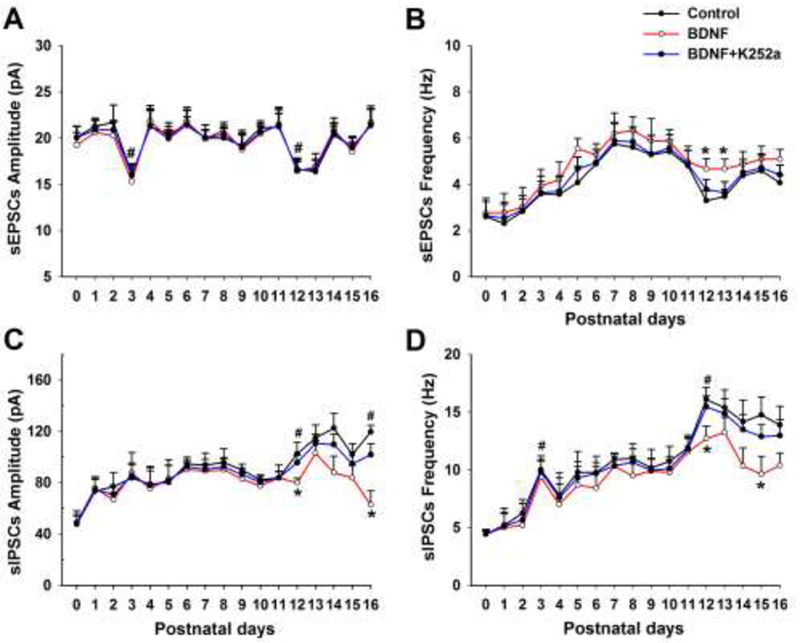
Mean amplitude and frequency of sEPSCs (A and B, respectively) and sIPSCs (C and D, respectively) from P0 to P16 before (control) and after BDNF or BDNF + K252a application in hypoglossal motoneurons. BDNF induced a significant rise in the frequency of sEPSCs at P12-13 (B) but a significant fall in the amplitude of sIPSCs at P12 and P16 (C) as well as the frequency of sIPSCs at P12 and P15 (D) when compared to controls (*P < 0.05). These effects were blocked by K252a. (modified from Gao et al., 2014).
