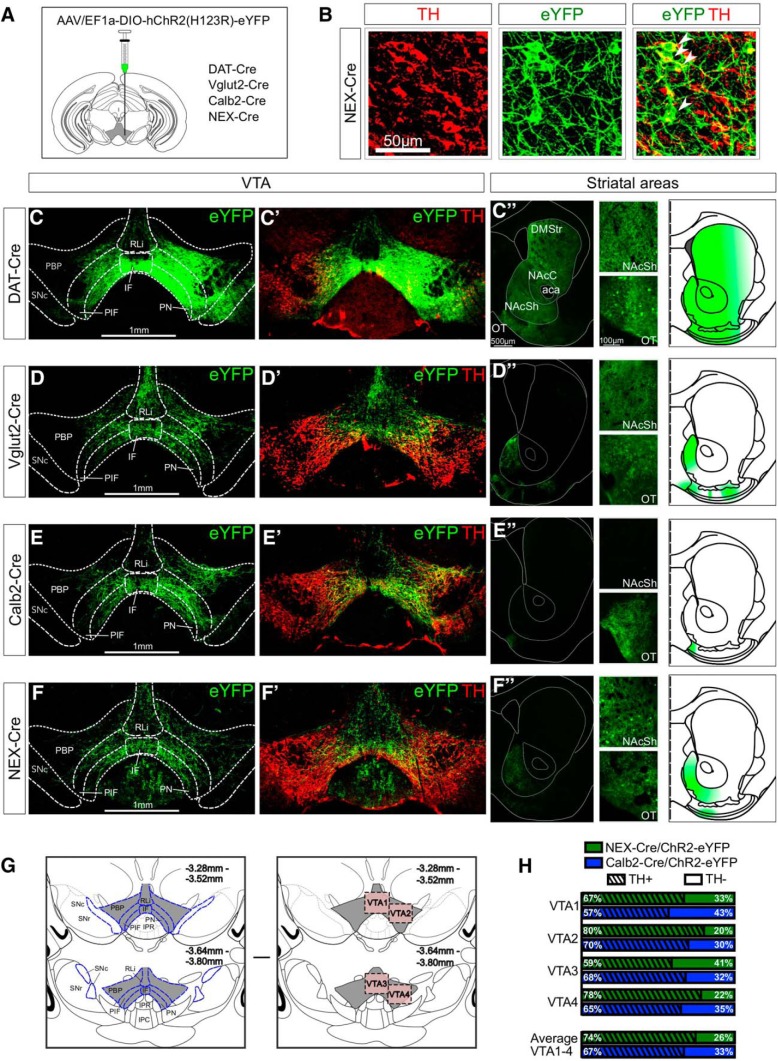
Figure 5.
Spatially restricted striatal innervation by NeuroD6 and Calb2 VTA neurons. A, Schematic illustration of stereotaxic injection into VTA of Cre-dependent DIO-ChR2-eYFP DNA construct packaged into AAV. B, Representative VTA neurons immunopositive for TH (red), YFP (green), or both (yellow; DIO-ChR2-eYFP-injected NEX-Cre mice). C–F, Representative pictures of VTA (left panels) and striatal complex (right panels) in DIO-ChR2-eYFP-injected DAT-Cre (C–C’’), Vglut2-Cre (D–D’’), Calb2-Cre (E–E’’), and NEX-Cre (F–F’’) mice. Panel far right, Schematic summary of striatal innervation pattern. Additional target areas listed in Table 2. Quantification of YFP and TH immunofluorescent overlap: schematic illustration of four representative VTA areas selected for counting, shown as squares and labeled VTA 1–4 (G). Results of quantifications shown in histograms for each VTA area and the total sum (H). PBP, parabrachial pigmented nucleus; PN, paranigral nucleus; PIF, parainterfascicular nucleus; RLi, rostral linear nucleus; IF, interfascicular nucleus; SNc, substantia nigra pars compacta; SNr, substantia nigra pars reticulata; IPR, interpeduncular nucleus, rostral subnucleus; IPC, interpeduncular nucleus, caudal subnucleus; DMStr, dorsomedial striatum; NAcC, nucleus accumbens core; NAcSh, nucleus accumbens shell; aca; anterior commissure, anterior part; OT, olfactory tubercle. DAT, Dopamine transporter, Calb2, Calbindin 2 (Calretinin); NEX, NeuroD6; Vglut2; Vesicular glutamate transporter 2; Th, Tyrosine hydroxylase; ChR2; Channelrhodopsin 2; eYFP, enhanced Yellow fluorescent protein.