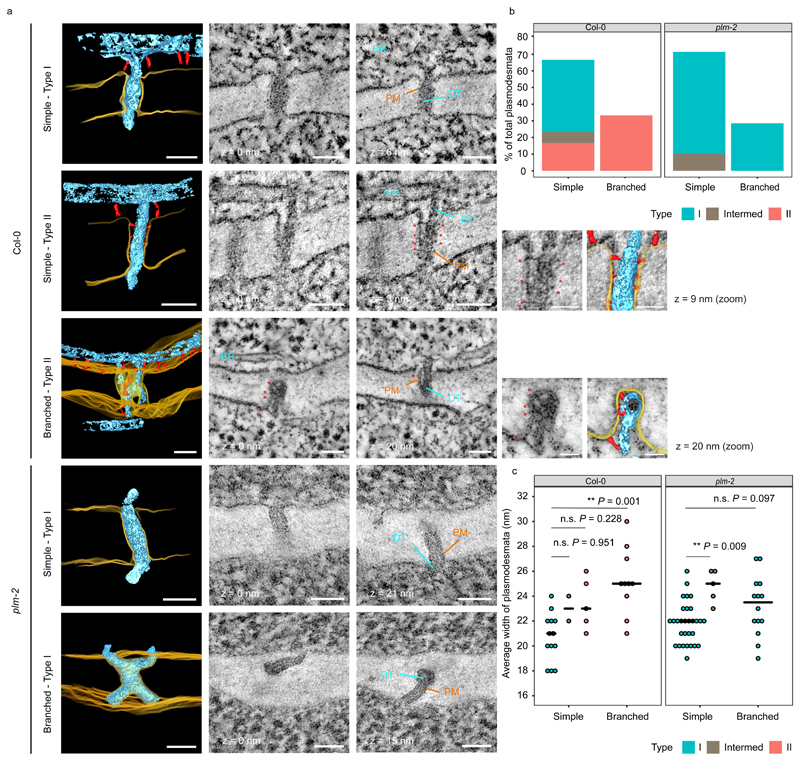
Figure 5. plm-2 lacks type II plasmodesmata at the PPP-endodermal interface of the unloading zone.
a. Plasmodesmata representing the various classes detected in Col-0 and plm-2 roots with electron tomography at the PPP-endodermal interface, within the unloading domain. Panels with black background are 3D reconstructions based on 2D image stacks. Note that the 3D view of the branched plasmodesmatata in Col-0 is tilted relative to 2D images for ease of visualisation. Plasma membrane (PM) is rendered in yellow, desmotubule (DT) and ER in light blue, tethers within plasmodesmata and outside of them in red. Selected 2D views are displayed in the neighbouring panels with zooms for tethers within type II plasmodesmata (with a model overlay). Distance to the first 2D view is indicated under or next to each panel. Arrows, symbols and labels indicate various plasmodesmata components and follow the colour scheme of the 3D models (* tether elements within plasmodesmata). Scale bars are of 50nm or 25nm for the zoomed panels. b. Quantification of morphologies and types of plasmodesmata present at PPP-endodermal interface within the unloading domain in Col-0 and plm-2 roots. n=30 (Col-0), n=49 (plm-2) plasmodesmata. The sections with plasmodesmata were acquired from two roots for each genotype. c. Comparison of the widths of plasmodesmata described in panel b. Median values for each group is represented by black horizontal bars. Significant differences in reference to simple (type I) plasmodesmata in Col-0 or plm-2 were determined by two-sided Dunn’s test. The P-values were adjusted with Holm method for multiple comparisons. ** P<0.01, n.s. no significance.