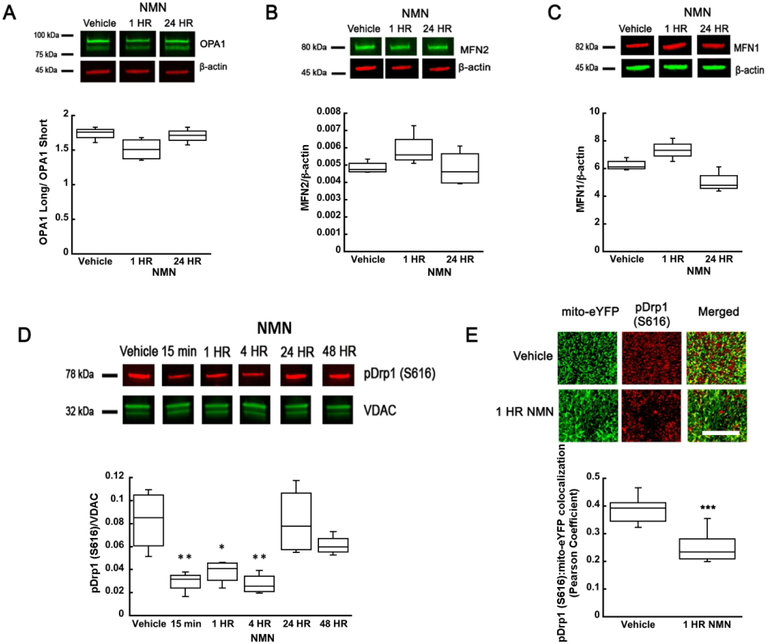
Figure 2.
NMN-induced changes in mitochondrial fusion and fission protein levels. NMN administration did not significantly affect OPA1 (A), MFN2 (B), or MFN1 (C) protein levels in hippocampal tissue. (D) However, the mitochondrial pDrp1 (S616) levels show a significant reduction from 15 min to 4 hours after NMN administration. At 24 and 48 hours the pDrp1 (S616) levels returned to control values. (E) Brain sections from the mito-eYFP (neuronal mitochondria-green) mice treated with NMN or vehicle (PBS) were immunostained with pDrp1 (S616) antibody (red). Z-stack images were collected and colocalization of pDrp1 (S616) with mito-eYFP in the CA1 oriens was quantified using Volocity software. NMN decreased colocalization of pDrp1 (S616) with mitochondrial eYFP as determined by the Pearson colocalization coefficient. Scale bar represents 100 μm. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 compared to vehicle (n=12 (A-C), n=24 (D), n=31 (E)) ((A-D) One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey HSD test, (E) Student T-test).