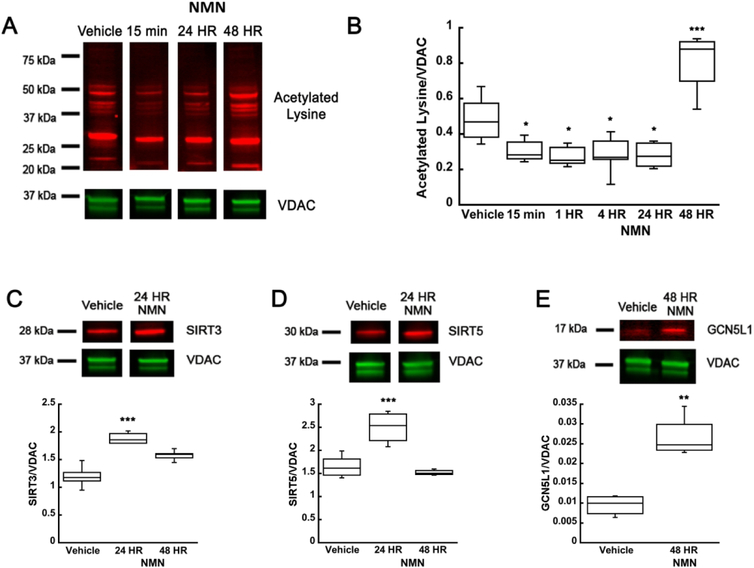
Figure 4.
NMN causes decrease in hippocampal mitochondria protein acetylation. (A) Western blot of hippocampal mitochondria samples that were collected after vehicle or NMN (62.5 mg/kg) administration at 15 min, 1, 4, 24, and 48 hours post-treatment. (B) Quantification of changes in mitochondrial protein acetylation NMN induced reduced acetylation of mitochondrial proteins at 15 min post-treatment. However, at 48 hours post-administration mitochondrial acetylation significantly increased when compared to vehicle treated animals. There was an increase in protein levels of mitochondrial deacetylases, SIRT3 (C) and SIRT5 (D) at 24 HR following NMN injection. However, the mitochondrial acetyltransferase, GCN5L1, expression levels were elevated 48 hours following NMN administration (E). * p<0.05, ** p<0.01 compared to vehicle (n=32 (B), n=16 (C), n=15 (D), n=7 (E)) (B One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey HSD test, C-E Student T-test).