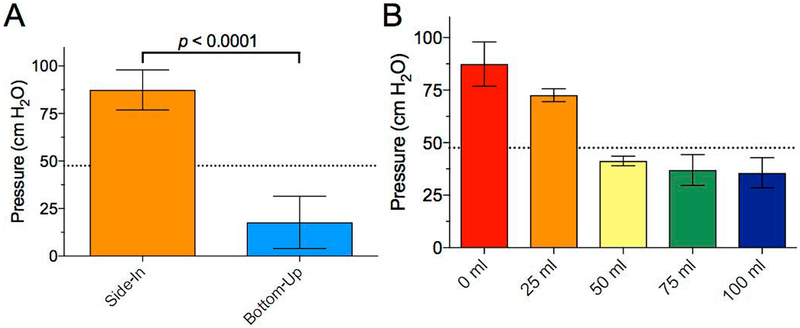
Figure 4 – The performance of the JP drain can be significantly affected by the methods of charging the bulb as well as the amount of fluid that has accumulated.
A) Maximum negative pressure generated by bulb compression via side-in and bottom-up compression methods. B) Negative pressure measurements with increasing amounts of JP bulb filling. The dashed line represents approximate level of suction accomplished by low intermittent wall suction for comparison (47.5 cm H2O). Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.