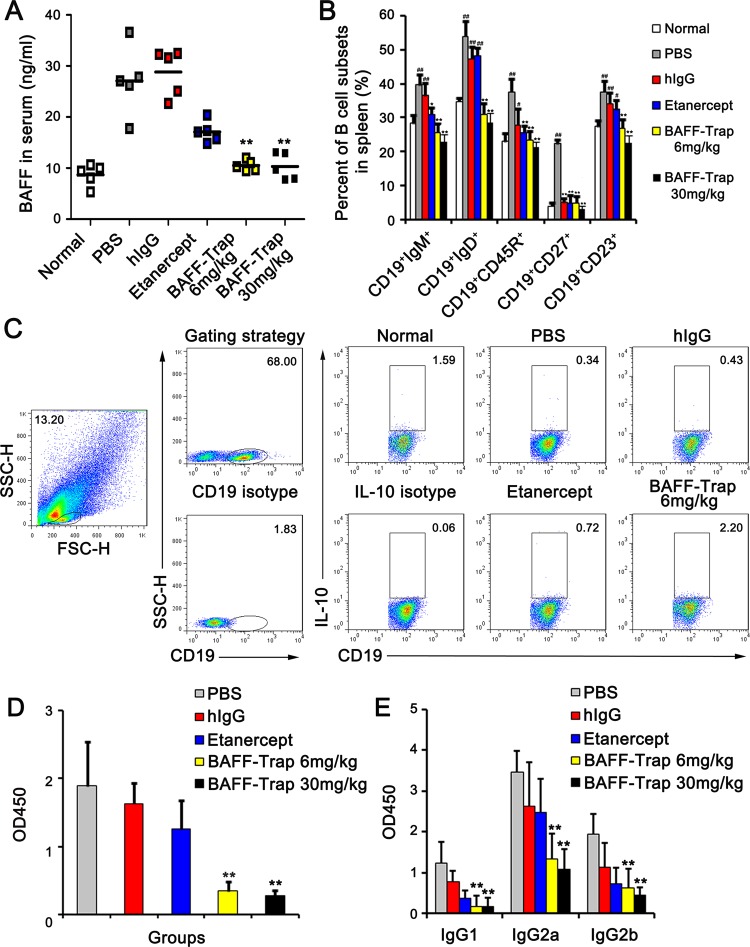
Fig. 4.
BAFF-Trap regulates B cells development and autoantibody production through reducing BAFF levels. a The protein levels of BAFF in serum from CIA mice treated with PBS, hIgG, Etanercept, and BAFF-Trap (6 mg/kg and 30 mg/kg). On day 42 after the indicated treatments, the serum of CIA mice was obtained. The levels of BAFF were detected by ELISA. b Percentage of B-cell subsets in spleen. On day 42 after the indicated treatments, mice were killed to obtain splenocytes. Then the splenocytes were incubated with corresponding antibodies to detect the subsets of B cells. Bars represent mean ± S.D. (n = 5). c Representative FACS analysis of Breg cells from joints. After digested by collagenase type IV, the cells in joint were obtained and incubated with corresponding antibodies to detect Breg cells. CD19+IL10+ cells meant Breg cells. Bars represent mean ± S.D. (n = 5). d The level of anti-CII IgG in serum obtained on day 42 after treatment. Serum was diluted to 1:10,000, and then anti-CII IgG concentrations were determined by ELISA. e The concentrations of anti-CII isoforms (IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b) on day 42 after indicated treatments. e TNF-α, f IL-1β, and g IL-6 concentration in serum from CIA mice, measured once every 7 days beginning on the first day of immunization. Bars represent mean ± S.D. (n = 5). #P < 0.051 versus normal; ##P < 0.01 versus normal; *P < 0.05 versus PBS; **P < 0.01 versus PBS