Fig. 1.
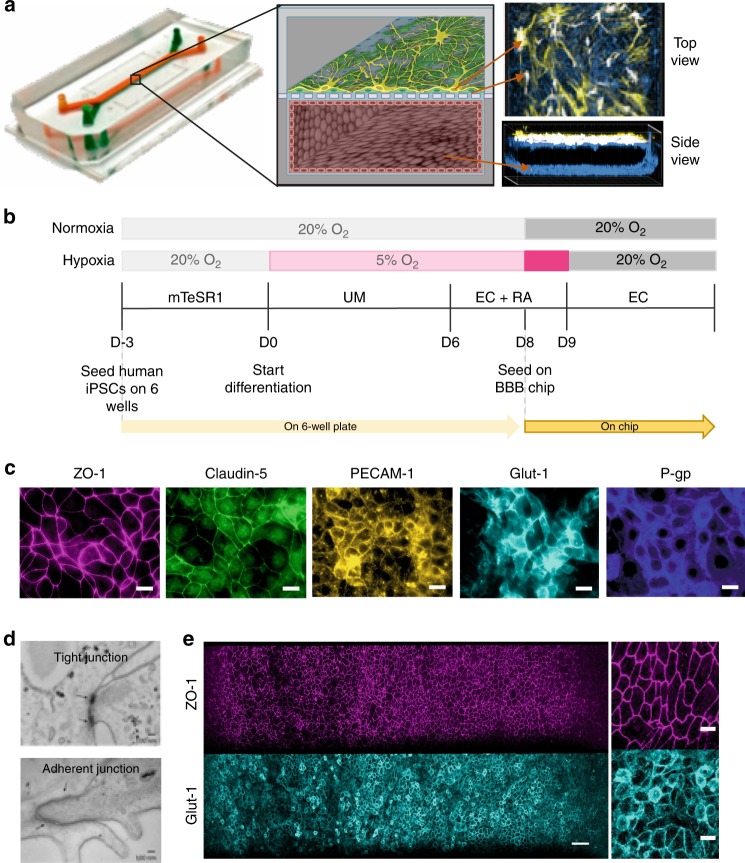
Reconstitution of the human BBB in an Organ Chip microfluidic device. a Photograph (left), schematic illustration (center), and immunofluorescence micrographs (right) of a 2-channel microfluidic Organ Chip with iPS-BMVECs cultured on all surfaces of the basal vascular channel, and primary human brain astrocytes and pericytes on the upper surface of the central horizontal membrane in the apical parenchymal channel. At the top right, z-stack images of the pericytes (yellow, F-actin staining) and astrocytes (white, GFAP staining) in the top channel of the BBB Chip are reconstituted and shown from above; a side view of similar stacked images for the lower vascular channel containing BMVECs (blue, ZO-1 staining) is shown at the bottom right. A video of overlay z-stack reconstituting this 3D BBB can be seen in Supplementary Movie 1. b Timeline for the in vitro differentiation of the human iPS-BMVECs, and seeding in the BBB Chips. c Immunofluorescence micrographs of the human brain endothelium cultured on-chip for 3 days labeled with ZO-1, Claudin-5, PECAM-1, GLUT-1, and P-glycoprotein (bar, 20 µm). d Electron micrographs of the human brain microvascular endothelium after 3 days in the BBB Chip, highlighting the presence of well-formed tight junctions (top, arrow) and adherens junctions (bottom, arrow) (bar, 100 nm). e Low (left) and high (right) magnification immunofluorescence micrographic views of the human brain microvascular endothelium cultured on-chip for 3 days viewed from above demonstrating high levels of expression of ZO-1 and GLUT-1 across the entire endothelial cell monolayer (bar, 50 µm)