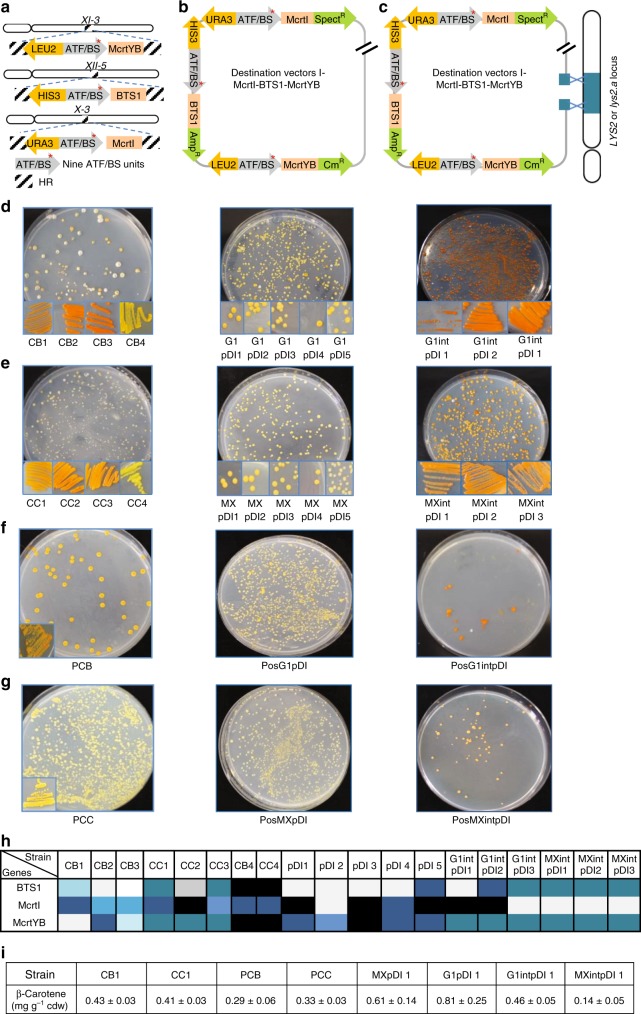
Fig. 5.
β-Carotene pathway optimization using COMPASS. a Overview of the three-gene β-carotene pathway library with integration of the genes into the X-3 (McrtI), XI-3 (McrtYB), and XII-5 (BTS1) loci (approach 1), b assembled in Destination vector I (pDI) (approach 2), or c assembled in pDI followed by integration into the LYS2/lys2.a locus (approach 3). URA3, LEU2, and HIS3 allow selection on SC-Ura/-Leu/-His media, while E. coli markers SpectR, AmpR, and CmR allow selection on LB media containing ampicillin, chloramphenicol, and spectinomycin. For simplicity, the IPTG-inducible promoters upstream of ATF/BSs, terminators, and cleavage sites flanking pathway genes are not shown. d β-Carotene production controlled by the nine ATF/BS units in strain Gen 0.1 or e IMX672.1. CB1–3 and CC1–3 (left plate), G1intpDI1–3 and MXintpDI1–3 (right plate) represent colonies with deep-orange colors from libraries containing randomized ATF/BSs upstream of β-carotene CDSs, while CB4 and CC4 represent modules expressing β-carotene CDSs from strong ATF/BSs. The plasmid libraries obtained with approach 2 were transformed into both background strains. Plasmid libraries extracted from the yeasts were transformed into E. coli. Five sequenced plasmids (pDI1–5, middle plate) were retransformed into both background strains to achieve strains G1pDI1–5 and MXpDI1–5. f Modules containing β-carotene CDSs under the control of the constitutive yeast TDH3 promoter were engineered into strains Gen 0.1 or g IMX672.1 to obtain PCB and PCC (left plate), PosG1pDI and PosMXpDI (middle plate), PosG1intpDI and PosMXintpDI (right plate). h Identification of ATF/BS units. The color code is given in Supplementary Fig. 1. i HPLC analysis of for three different colonies of strains. Gray arrows, nine ATF/BS units. Black/white-striped squares, homology regions. Data are means ± SD from three biological replicates