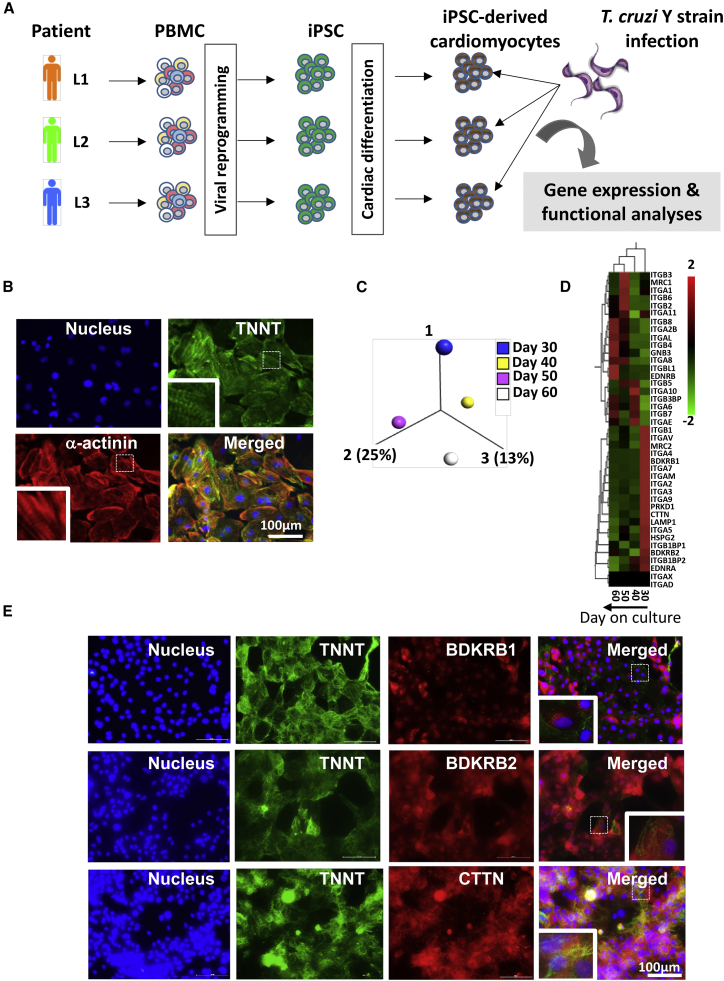
Figure 1.
Human iPSC-CMs and Receptors to Trypanosoma cruzi Invasion
(A) Overview of study design. PBMCs from three healthy individuals were reprogrammed to iPSCs using a Sendai virus vector expressing Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc. iPSC clones were differentiated into iPSC-CMs, infected with T. cruzi Y strain, and submitted for gene expression and functional analysis.
(B) Immunofluorescence images of iPSC-CMs confirming the presence of sarcomeric proteins such as α-actinin and troponin T.
(C and D) Variability in gene expression of receptors for T. cruzi invasion on iPSC-CMs cultured on days 30, 40, 50, and 60. (C) PCA with computation of closest neighboring samples; (D) heatmap showing hierarchical clustering between iPSC-CMs cultured on different days.
(E) Immunofluorescence images of iPSC-CMs showing the expression of receptors to T. cruzi such as bradykinin receptor 1 (BDKR1), bradykinin receptor 2 (BDKR2), and cortactin (CTTN). The expression of TNNT was used as a control. Scale bars, 100 μm.