FIGURE 1.
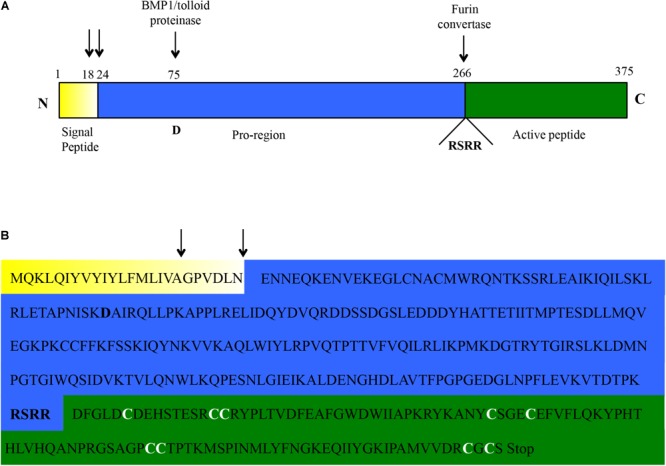
Amino acidic sequence of the C. dromedarius myostatin as inferred from the cDNA sequence. (A) Schematic outline. The three protein domains (signal peptide, pro-region, and active peptide) are highlighted in different colors (yellow, blue, and green, respectively). The two most likely residues involved in the signal peptide cleavage (see main text) are indicated by black arrows. Similarly, the residue (D, for aspartic acid) shown to be essential for BMP/tolloid protease cleavage, and the motif (RSRR) needed for recognition by furin convertase, are highlighted. (B) Amino acidic sequence of the C. dromedarius myostatin, with the three protein domains highlighted in different colors, as in (A). The above mentioned hallmarks are also depicted here (signal peptide cleavage, black arrows; BMP/tolloid protease cleavage residue and furin convertase recognition motif, bold). In addition, the nine conserved cysteine residues in the active peptide are indicated (bold and white).
