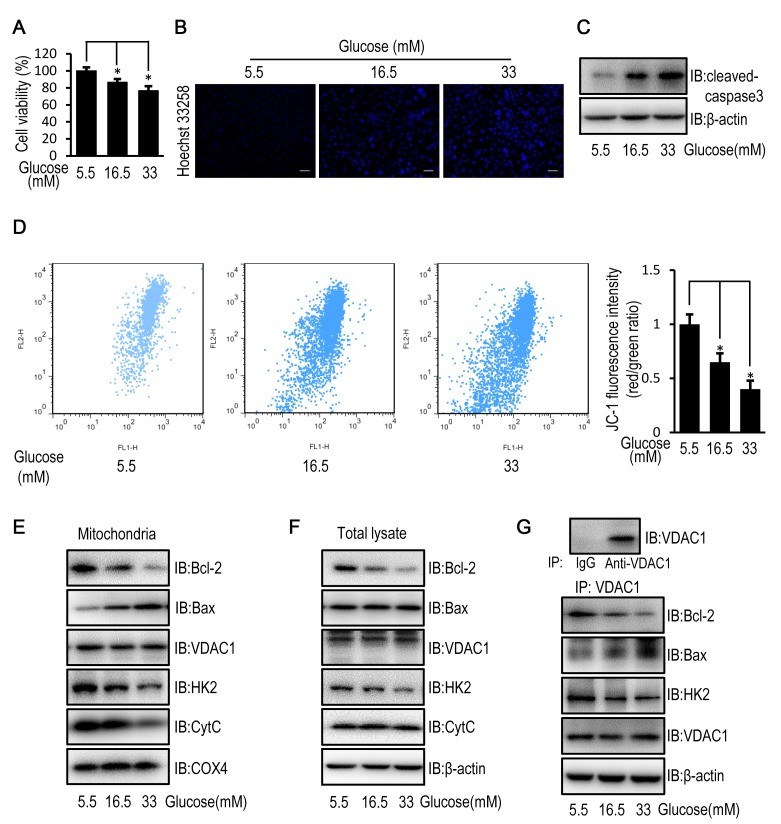
Figure 1.
High glucose induces apoptosis in HUVECs by disturbing the mitochondrial membrane potential. HUVECs were cultured in DMEM containing 5.5, 16.5 or 33 mM glucose for 72 h. (A) MTT assay was used to examine cell viability of HUVECs. (B) Cell apoptosis was examined in HUVECs stained with the fluorescent nuclear dye Hoechst 33258. Scale bar=200 mm. (C) The protein expression level of cleaved caspase-3 was determined by western blot analysis in HUVECs. (D) Mitochondrial membrane potential was examined in HUVECs following JC-1 staining and flow cytometric analysis for fluorescence emission at 530 nm (JC-1 FL1) and 575 nm (JC-1 FL2). The FL2/FL1 ratio represents mitochondrial membrane potential. (E) The protein expression level of Bcl-2, Bax, VDAC1, HK2, CytC and COX4 were determined by western blot analysis in mitochondria isolated from HUVECs. (F) The protein expression levels of Bcl-2, Bax, VDAC1, HK2 and CytC were determined by western blot analysis in HUVECs. (G) The protein expression level of Bcl-2, Bax, HK2 and VDAC1 were determined by western blot analysis in HUVECs following immunoprecipitation with VDAC1 antibody. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error. *P<0.05 as indicated. HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cell; DMEM, Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium; Bax, Bcl-2 associated X; VDAC1, voltage-dependent anion channel 1; HK2, hexokinase 2; CytC, cytochrome c; COX4, cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4; IB, immunoblotting.