Figure 2.
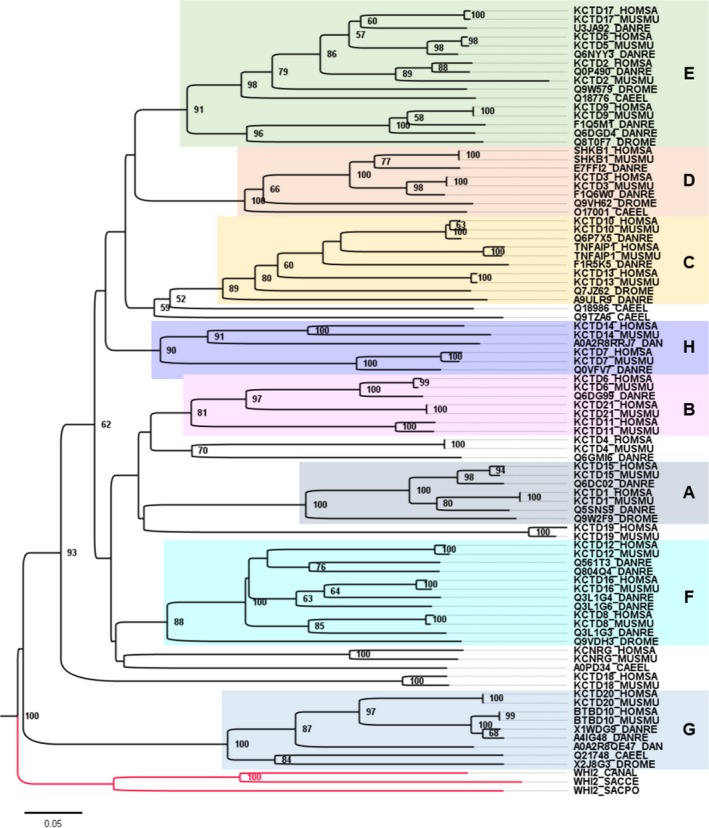
Phylogenetic tree of isolated BTB domains from KCTD family homologs. Amino acid sequences of KCTD family proteins from human (Homo sapiens, HOMSA), mouse (Mus musculus, MUSMU), zebrafish (Danio rerio, DANRE), Drosophila melanogaster (DROME), Caenorhabditis elegans (CAEEL), and three yeast species (Saccharomyces cerevisiae, SACCE; Schizosaccharomyces pombe, SACPO; Candida albicans, CANAL) were collected from UniProt (release 2019_02) or after searches using the DELTA‐BLAST algorithm on the NCBI website. Sequences were aligned using MAFFT (version 7), and a neighbor‐joining (NJ) analysis was performed with 1000 bootstrap replicates. Bootstrap support values above 50 are shown at each node. The tree was rooted using Whi2p from S pombe. Yeast sequences were represented as an outgroup (red branches). The arbitrary cluster designations for groups A‐G were assigned to match those reported by Skoblov et al.1 The new H group is deduced from this analysis. Compared to Skoblov et al,1 we found that KCTD9 segregates within group E. Amino acid sequences (Table S1) and alignment results (Table S2) for this analysis are found in Supporting information
