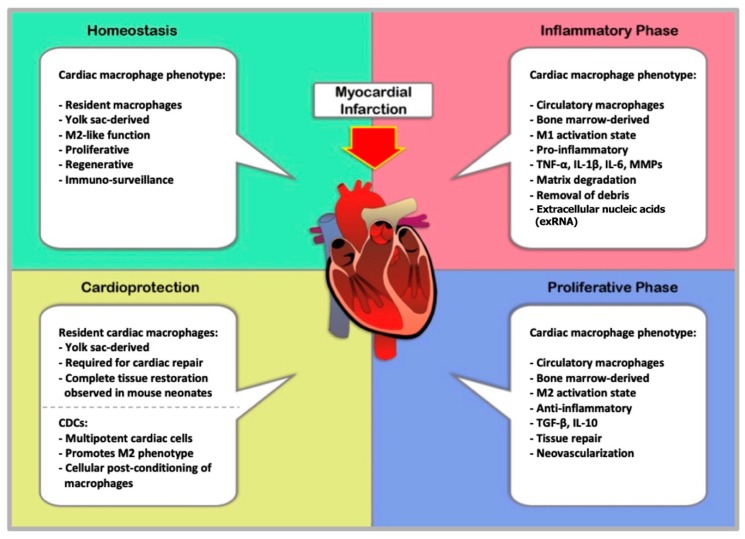
Figure 1.
The Cardiac macrophage population, while the heart is in homeostasis, consists primarily of yolk sac-derived macrophages. However, these resident tissue macrophages diminish in number with age and are replaced by circulating bone marrow-derived monocytes even in the absence of inflammation. BMDM replenish the cardiac macrophage supply, and exhibit M2 activation in the steady-state heart. The inflammatory phase of acute myocardial infarction initiates an immune response by monocytes/macrophages, which are recruited to the injured tissue. Ly6CHigh monocytes infiltrate and accumulate in the injured area where they differentiate into “classical” M1 macrophages. M1 macrophages secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines and MMPs upon activation by DAMPs. The inflammatory response peaks at around day 5–7 and ultimately results in clearance of dead cells and cell debris, processes essential for tissue repair. Resolution of inflammation after MI marks the beginning of a proliferative phase. During which, circulating Ly6CLow monocytes infiltrate the infarcted area. Thus, the population of cardiac macrophages begins to move toward alternative activation. The presence of M2 macrophages suppresses inflammation, enhances tissue repair and promotes angiogenesis by the expression of TGF-β and IL-10. Dysregulation of either the inflammatory or proliferative phase can produce severe outcomes like ventricular weakening, fibrosis, and compromised function. Macrophages can participate in cardioprotection via cell-mediated mechanisms. For example, yolk sac-derived cardiac macrophages are required for reparative mechanisms of wound healing. Further, the identical phenotype in murine neonates has full regenerative capacity after MI and remains through adulthood although it diminishes greatly over time and post-MI. CDCs are another example of cellular cardioprotection. The cardiac type of mesenchymal stem cell, CDCs have the potential to induce M2 activation in macrophages. Post-conditioning of macrophages with CDCs results in an alternatively activated phenotype, which has been shown to improve prognosis following myocardial infarction. Abbreviations: BMDM; bone marrow derived macrophages, DAMP; damage associated molecular pattern, MMP; metallo-matrix proteinase; IL-10; interleukin-10, TGF-β; transforming growth factor-β, CDC; cardiosphere-derived cells.