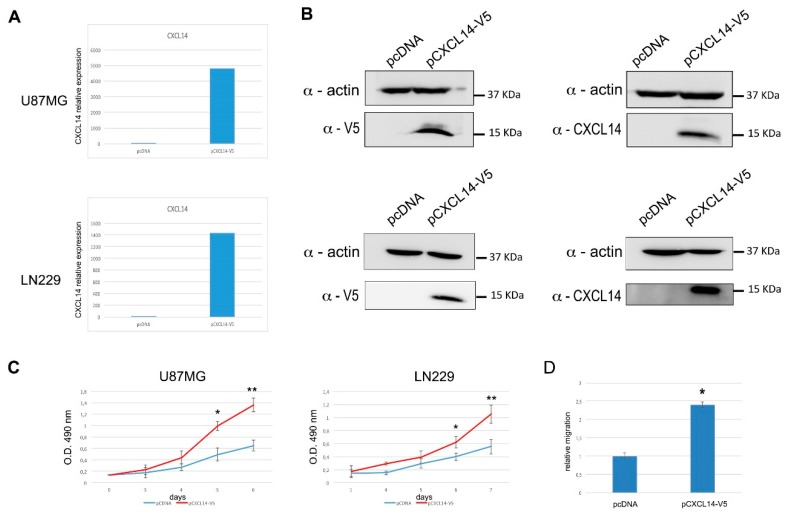
Figure 5.
Glioblastoma cells stably overexpressing CXCL14 show enhanced proliferation and migration. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of CXCL14 mRNA expression in U87MG (upper panel) or LN229 (lower panel) cells transfected with either the empty vector pcDNA3.1/V5-HisC (pcDNA), or the CXCL14-expressing vector pCXCL14-V5. In both panels, data are expressed as compared to empty vector-transfected cells, where CXCL14 expression was set as = 1. (B) Western blot analysis showing CXCL14 protein expression in U87MG (upper panel) or LN229 (lower panel) cells transfected with either the empty vector pcDNA3.1/V5-His C, or the CXCL14-expressing vector pCXCL14-V5. In the immunoblots shown on the left, ectopic CXCL14 was revealed by using an anti-V5 antibody, while on the right a CXCL14-specific antibody was used. β-actin detection was used as a loading control. (C) Proliferation (MTS assay) of U87MG (left) or LN229 (right) cells stably transfected with either the empty vector pcDNA3.1/V5-His C, or the CXCL14-expressing vector pCXCL14-V5. Results are shown as the mean ± S.D. and represent the average of two experiments performed in triplicate. Data were analyzed by a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. * p < 0.05 ** p < 0.01. (D) Boyden chamber migration assay performed with U87MG cells stably transfected with either the empty vector pcDNA3.1/V5-HisC (pcDNA), or the CXCL14-expressing vector pCXCL14-V5. The graph depicts the relative migration of CXCL14-expressing cells compared to empty vector transfected ones, whose migration ability was set as = 1. Results are presented as mean ± S.D. with significant differences from controls (*) shown (p < 0.05).