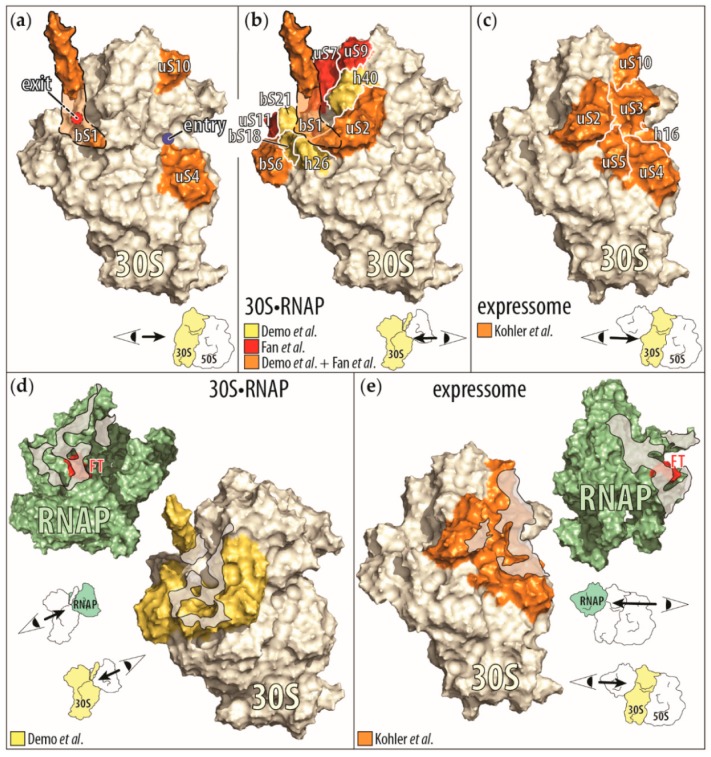
Figure 3.
Display of the RNAP-ribosome interactions and contact points identified by biochemical and cryo-EM studies. (a) Ribosomal proteins (in orange) that influence the RNAP activity by themselves (bS1 [65], uS4 [60], and uS10 [63]) are mapped onto the small ribosomal subunit (30S), derived from the cryo-EM structure of the small ribosomal subunit bound to the RNAP (30S•RNAP) [71]. Because ribosomal protein bS1 is only partially resolved in this structure, we outlined the approximate position of the remaining protein (orange shaded area). In addition, the mRNA entry (blue circle) and exit (red circle with dashed black border indicating its positions behind bS1) sites on the small ribosomal subunit are indicated. In the right corner is a cartoon representation of the direction of the view displayed of the small ribosomal subunit. (b) Ribosomal proteins and RNA helices contacting the RNAP upon binding of the small ribosomal subunit to RNAP. Shown are the proteins identified to be close to the RNAP in the cryo-EM structure of 30S•RNAP in Demo et al. [71] and by chemical crosslinking in Fan et al. [73]. (Proteins observed only in Demo et al. are in yellow, those shared by Demo et al. and Fan et al. are in orange, and those observed only in Fan et al. are in red.) (c) Ribosomal proteins (in orange) contacting the RNAP in the cryo-EM structure of a ribosome translating a nascent RNA as it is being synthesized, also known as expressome [72]. Interactions between the C-terminal domain of one of the two α subunits of the RNAP with the ribosome were omitted for clarity. (d,e) Contact interfaces between the RNAP and the small ribosomal subunit as seen in the cyro-EM structures of the 30S•RNAP complex (d) and the expressome (e). In both representations, the view is onto the contact areas (gray shaded areas) on the RNAP (green) and on the small ribosomal subunit (yellow). Also indicated is the β flap-tip of the RNAP (red, marked with FT), past which the nascent RNA exits the RNAP to enter the small ribosomal subunit.