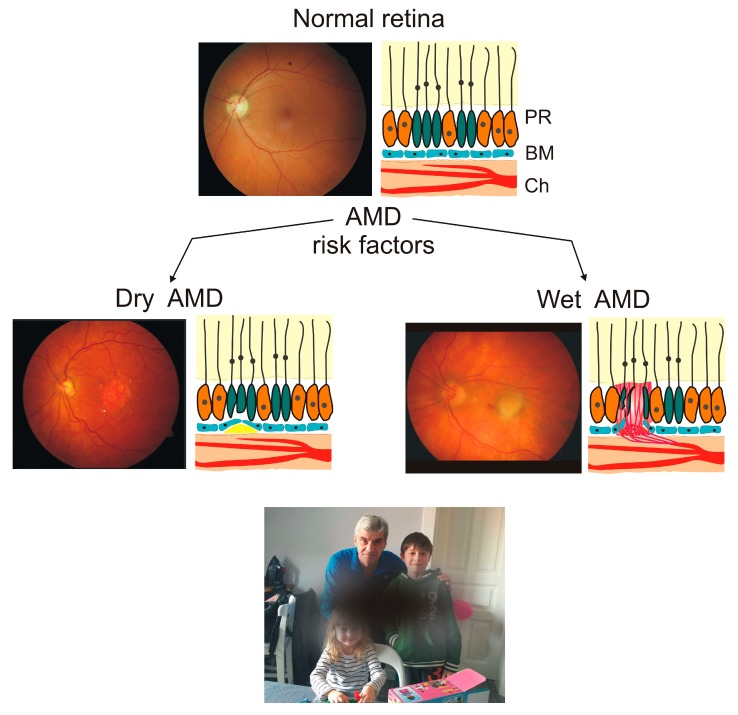
Figure 1.
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is an eye disease affecting the macula, a central region in the retina. Presented are color pictures of fundus for normal retina and retina with changes typical for dry and wet AMD, two of its basic, clinically distinguished categories. Dry AMD is typified by the presence of drusen, yellowish objects between choroid (Ch) and Bruch’s membrane (BM), and photoreceptor (PR) loss. Wet AMD is associated with abnormal angiogenesis (choroidal neovascularization), leading to bleeding resulting in lifting up the macula from its normal position. Individuals affected by AMD in its advanced stage may experience problems with central vision.