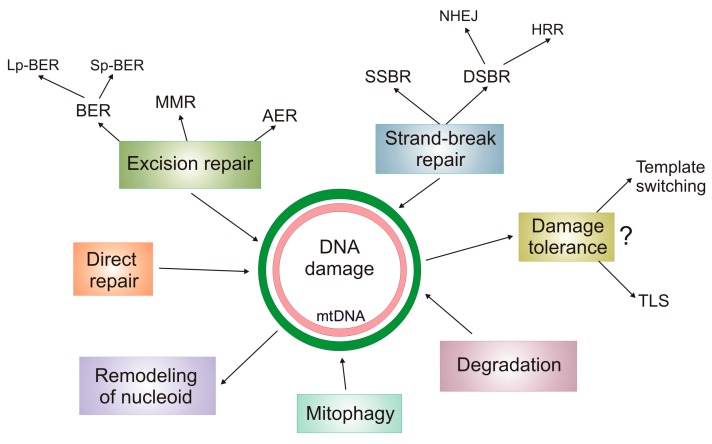
Figure 2.
DNA damage response in mitochondria (mtDDR). In general, DNA damage in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) can be repaired or tolerated. Highly damaged mtDNA can be degraded, and mitophagy can contribute to this process although its exact nature is unknown. BER—base excision repair; Lp and Sp—long and short patch, respectively; MMR—mismatch repair; AER—alternative excision repair; SSBR and DSBR—single- and double-strand break repair, respectively; NHEJ—non-homologous end joining; HRR—homologous recombination repair; TLS—translesion synthesis. Remodeling of mitochondrial nucleoid has not been shown as a mtDDR pathway, but it can be assumed that it occurs if needed. The mechanism of DNA damage tolerance is hardly known in mtDNA, symbolized by a question mark.