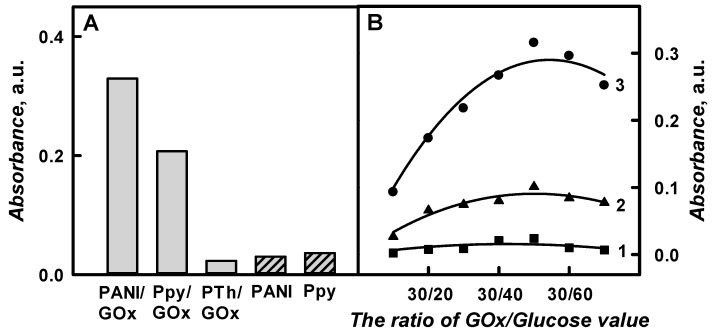
Figure 5.
The diagram of optical absorbance of PANI-, Ppy-, and PTh-based composite nanoparticles in the presence and absence of GOx (A) and the influence of GOx/Glucose ratio on the absorbance for PTh/GOx (1 curve), Ppy/GOx (2 curve), or PANI/GOx (3 curve) composite nanoparticles colloidal solutions at pH 6.0 (B). ((A) The composition of polymerization solution, pH 6.0: 0.05 mol L−1 of glucose, 0.50 mol L−1 of aniline, pyrrole, or thiophene and 0.75 mg mL−1 of glucose oxidase (grey columns); the composition of solution used for autopolymerization: 0.05 mol L−1 of glucose, 0.50 mol L−1 of aniline or pyrrole at pH 1.0 or pH 2.0, respectively (dash columns); (B) The composition of polymerization solution, pH 6.0: 0.50 mol L−1 of aniline, pyrrole or thiophene, 0.75 mg mL−1 of glucose oxidase and 0.015–0.05 mol L−1 of glucose. Polymerization lasted for 48 h. Optical absorbance was registered for PANI/GOx and PANI, Ppy/GOx, and Ppy, PTh/GOx at λmax = 440 nm, λmax = 460 nm, and λmax = 450 nm in 0.05 mol L−1 SA buffer, pH 6.0).