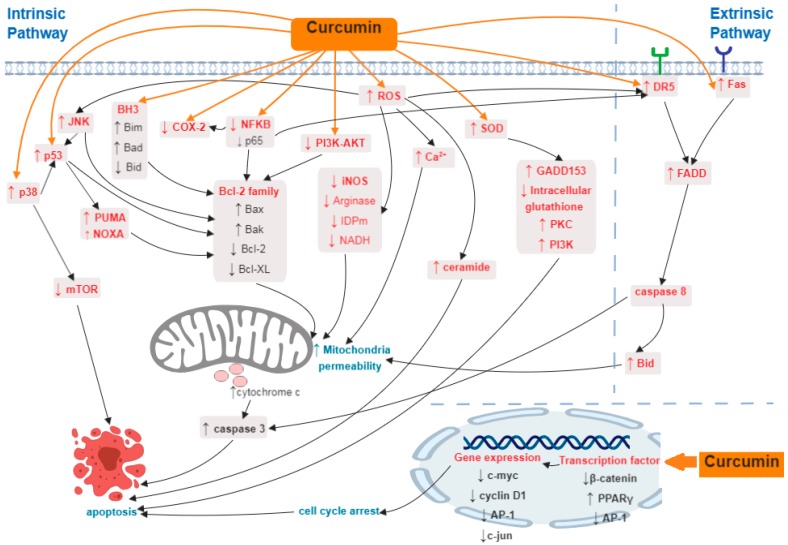
Figure 1.
Summary of induction of apoptosis by curcumin in colorectal cancer (CRC). Curcumin induces apoptosis in CRC through multiple target molecules and associated signaling pathways. Curcumin inhibits nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB)and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), down-regulates transcription factor β-catenin and activating protein-1 (AP-1), suppresses anti-apoptotic proteins and increase reactive oxygen species (ROS), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and pro-apoptotic proteins and also up-regulates Fas and death receptor 5 (DR5) receptor. Molecules in red represents the main targets of apoptosis while molecules in black are the downstream targets of the molecules labelled in red.