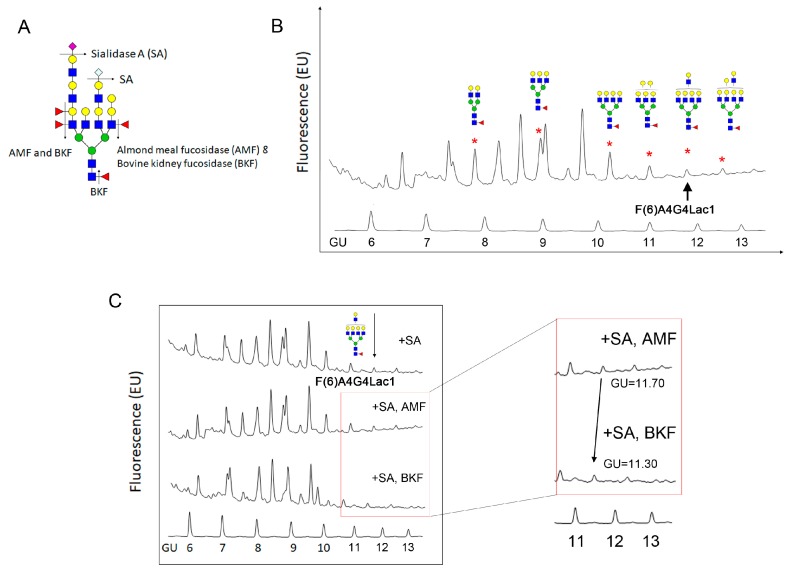
Figure 3.
N-glycan sequencing of 4T1 cells. (A) Exoglycosidase enzymes used in this experiment. Sialidase A (SA) was used to remove mammalian N-acetyl neuraminic acid (NeuAc) or N-glycolylneuraminic acid (NeuGc); almond meal fucosidase (AMF) was used to remove outer arm α-1,2-, 1,3- and 1,4- link fucose; bovine kidney fucosidase (BKF) was used to remove all fucose residues including core α-1,6-linked fucose. (B) N-glycan chromatogram of 4T1 cells after being treated with SA and AMF. Several core-fucosylated glycans with different modifications (i.e., biantennary, tri-antennary, tetra-antennary, galactose, lactosamine) attributed to ~27.1% of total glycan in 4T1 cells. (C) Exoglycosidase digestions of 4T1 cells revealed ~1.5% of the total glycan was core fucosylated tetra-antennary glycan with one lactosamine arm/F(6)A4G4Lac1 (marked with an arrow). Insert, AMF and BKF treated samples shown following BKF digestion peak 11.70 glucose unit (GU) shifted to 11.30 GU confirmed the loss of one fucose residue at the α-1,6-linkage.