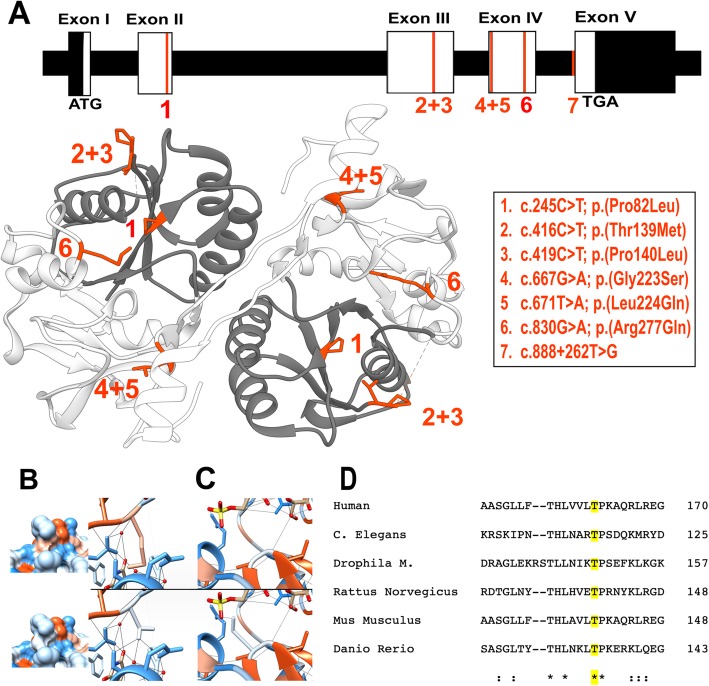
Fig. 3.
a Overview of all the known pathogenic mutations on a schematic representation of the cDNA and gDNA transcript of B3GAT3 on top and a representation of all missense mutations on an in silico model of GlcAT-I in which the substrate donor is colored in dark grey and the substrate acceptor subdomain is colored light grey. All mutations are highlighted in red. b-c In silico modelling. Hydrophilic residues are blue, hydrophobic residues are red. b p.Thr139 (top row) and the p.(Thr139Met) variant (below) with hydrophobicity surface rendering showing a change in the missense variant. The right column shows the disruption of 3 H-bonds in the missense variant. c The p.Gly223 residue (on top) and the p.(Gly223Ser) variant (below) showing the formation of a new H-bond. d Clustal Omega protein sequence aligment showing that the protein sequence of GlcAT-I is (largely) conserved across vertebrates and invertebrates. Asterisks indicate a single, fully conserved residue, colons indicate strong similar properties (> 0.5 on the Gonnet PAM 250 matrix), and periods indicate weak similar properties (< 0.5 in the Gonnet PAM 250 matrix). The sequence alignment shows the high conservation of the Thr residue on position 139 of the sequence (marked in yellow)