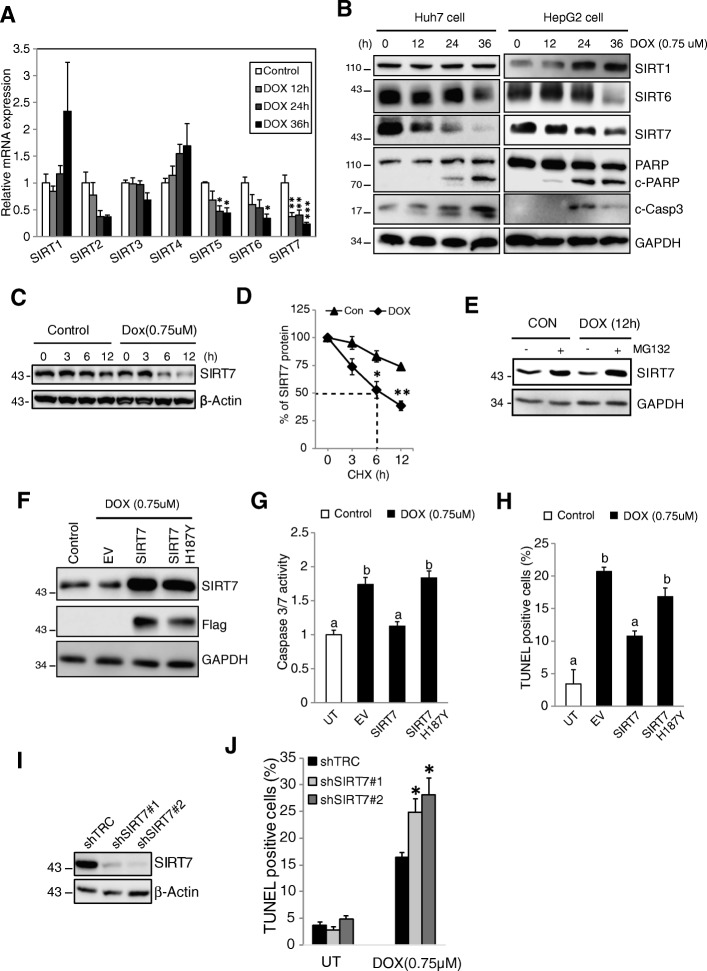
Fig. 2.
SIRT7 is critical in determining doxorubicin induced cell death. a Huh7.5 cells were untreated (Control) or treated with doxorubicin (DOX, 0.75 μM) for 36 h. Cells were harvested at various time points as indicated. mRNA levels of SIRT1-7 were evaluated by RT-PCR. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs Control, one way ANOVA. b HepG2 and Huh7.5 cells were treated with doxorubicin for various time and protein levels were evaluated by western blot. c and d SIRT7 protein half-life in Huh7.5 cells either untreated (Con) or treated with doxorubicin in the presence of cycloheximide (CHX, 100 μM). *P < 0.05, *P < 0.01 vs Con, Student’s t-test. e SIRT7 protein level in Huh7.5 cells either untreated (CON) or treated with doxorubicin for 12 h in the absence or presence of the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (50 μM). f-h Huh7.5 cells were untransfected (Control) or transfected with empty vector (EV), SIRT7 or SIRT7 187HY for 24 h, followed by doxorubicin treatment for another 36 h. Protein expression levels were evaluated by western blot (f) and cell death were evaluated by caspase 3/7 activity (g) and TUNEL assay (h). Values with different superscripts are significantly different from each other (p < 0.05, one way ANOVA). i and j Huh7.5 cells were treated with scramble shRNA (shTRC) or shRNA targeting SIRT7 (shSIRT7#1 and shSIRT7#2) for 72 h, SIRT7 levels were evaluated by western blot (i). Cells were then treated with doxorubicin for 36 h and cell death were evaluated by TUNEL assay (j). *P < 0.05 vs shTRC/DOX, one way ANOVA. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Graphs show mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments