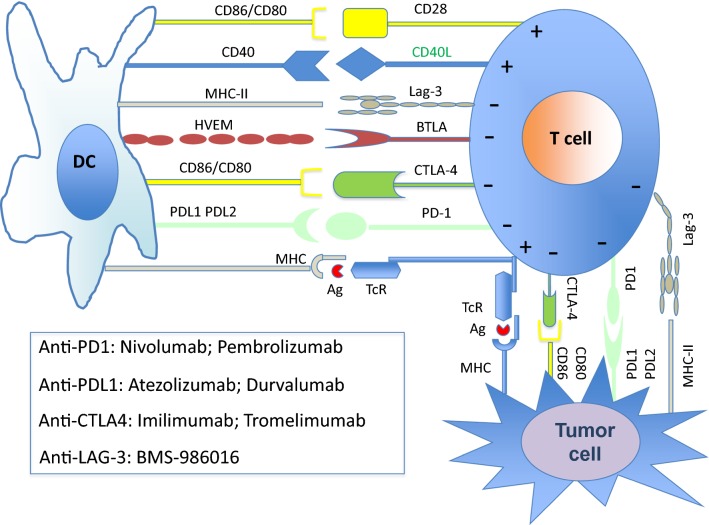
Fig. 5.
Illustration of the immune checkpoint molecules and their inhibitors. Immune checkpoint inhibitors are potent molecules implicated in the cell–cell communications. They are present on T-cells and their ligands are shared by tumor cells and dendritic cells (DC). Immune checkpoint molecules send negative signals to T cells and inhibit the later activities. Monoclonal antibodies have been developed against different molecules and used as therapeutic checkpoint inhibitors. CTLA-4: cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4, TcR: T cell receptor; MHC: major histocompatibility complex; HVEM: Herpes Virus Entry Mediator; PD1: programmed death; PDL-1/2: programmed death ligand-1/2; Lag-3: lymphocyte-activation gene 3; BTLA: B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator; Ag: antigen