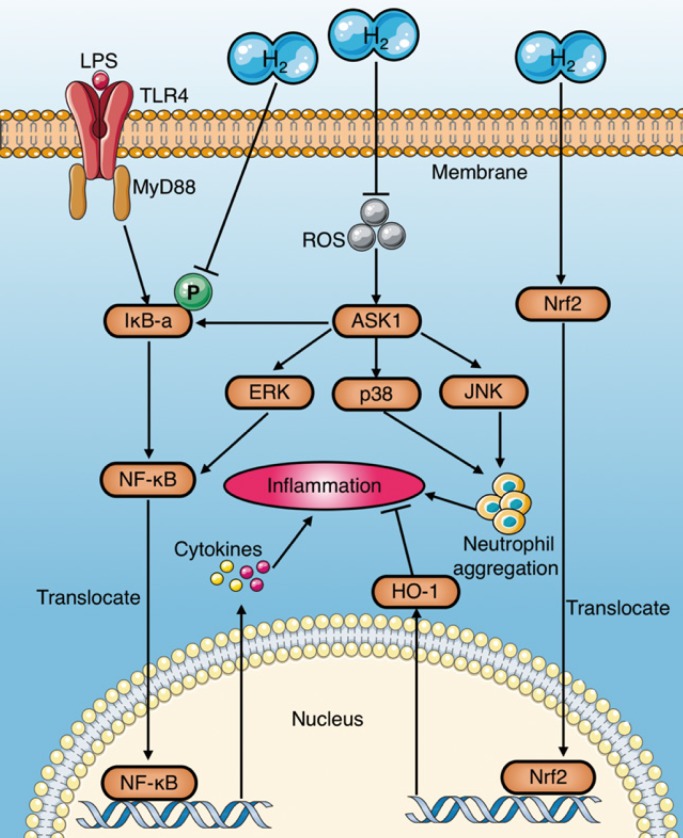
Figure 5.
Anti-inflammation mechanisms of molecular hydrogen during sepsis. (a) Molecular hydrogen suppresses the NF-κB pathway to reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines by inhibiting IκB-a phosphorylation or suppressing ERK activation mediated by upstream and ASK1. (b) Molecular hydrogen reduces neutrophil aggregation by inhibiting activation of ROS-ASK1-MAPK. (c) Molecular hydrogen attenuates the inflammatory response by activating the Nrf2-mediated HO-1 signaling pathway. ASK1: apoptotic signal-regulated kinase 1; ROS: reactive oxygen species; ERK extracellular regulated kinase; MAPK: mitogen activated protein kinase.