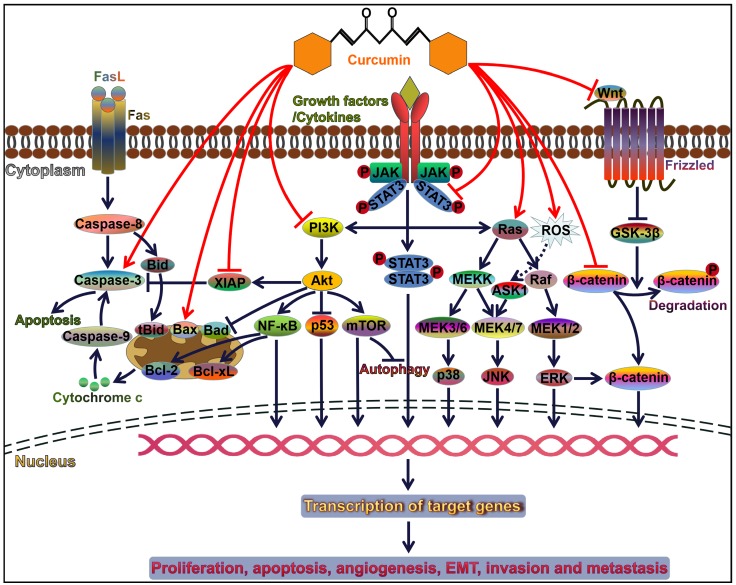
Figure 1.
Curcumin modulates cancer progression by controlling diverse signal transduction pathways. Attachment of ligands (e.g., growth factors and cytokines) to their corresponding receptors induces the activation of downstream signaling pathways, such as PI3K/Akt, JAK/STAT, and MAPK pathways. These pathways play an important role in cell survival, proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis. Curcumin can orchestrate these three pathways and thus serves a pivotal role in cancer progression. Akt activation restrains the p53 signaling and Bad-mediated apoptotic pathway contributing to cancer cell survival. Akt also initiates the NF-ĸB signaling pathway. NF-ĸB favors the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, thereby leading to the inhibition of cancer cell apoptosis. Curcumin acts as an inhibitor of NF-ĸB and functions in activating the caspase cascade. Therefore, curcumin facilitates cancer cell apoptosis. Wnt binds to Frizzled receptor to trigger the canonical Wnt pathway. In the absence of Wnt signaling, GSK3-β induces the phosphorylation of β-catenin and results in its degradation. Wnt binding to its receptor can inhibit the activation of GSK3-β, thus allowing stabilization and accumulation of β-catenin in the cytoplasm. Accumulated β-catenin eventually translocates into the nucleus and induces the expression of multiple oncogenes and EMT-inducing transcription factors. Curcumin is capable of repressing the EMT process in cancer cells through inactivation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. FasL, Fas ligand; Bid, BH3-interacting domain death agonist; tBid, truncated Bid; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma-2; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; Bad, Bcl-2-associated death promoter; Bcl-xL, B-cell lymphoma-extra-large; XIAP, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; Akt, protein kinase B; NF-ĸB, nuclear factor-ĸB; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; JAK, Janus kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; MEKK, MEK kinase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; ASK1, apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β.