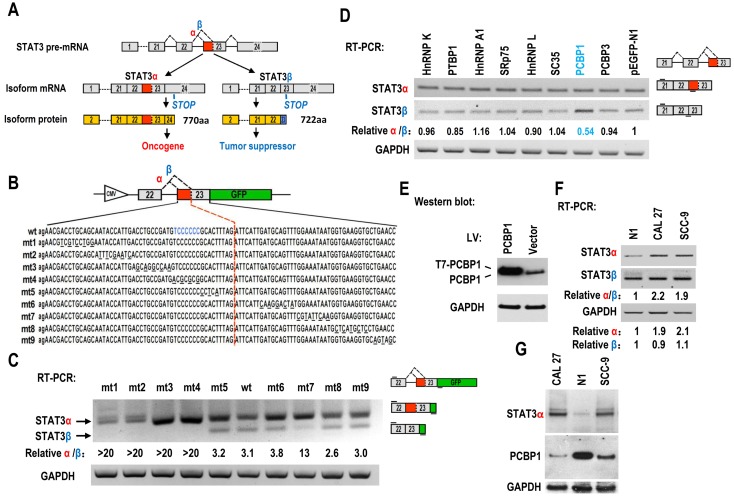
Figure 1.
Screening of key motifs in STAT3 exon 23 and splicing factors which are responsible for regulating the alternative splicing of STAT3 exon 23. (A) Schematic diagram of the alternative splicing pattern of human STAT3 exon 23. The boxes represent exons, and the solid lines between the boxes represent the introns. The dashed lines above the introns indicate the direction of RNA splicing. STOP represents the terminating codons. Isoform STAT3α mRNA encodes an oncoprotein, while isoform STAT3β encodes a tumor suppressor. (B) Diagram of STAT3 minigene. Genomic sequence of STAT3 from 3′ part of exon 22 to 5′ part of exon 23 was amplified from CAL 27 cells and cloned into pEGFP-N1. To map potential regulatory motifs, exon 23 in minigene was serially mutated. The mutated bases were underlined. (C) RT-PCR analysis of alternative splicing of exon 23 in HEK293 cells transfected with wild-type (wt) or mutant (mt) minigenes. Relative α/β represents the ratio of band intensities of isoform α vs β. GAPDH served as a loading control. Diagrams on the right show the structures of STAT3 minigene and spliced products. Short line above exon 22 stands for the forward primer, and short line below GFP gene stands for the backward primer. (D) Screening analysis for splicing factors which regulates alternative splicing of STAT3 exon 23. HEK293 cells were transfected with indicated RNA splicing factors or control plasmid (pEGFP-N1). Alternative splicing of endogenous STAT3 exon 23 was analyzed by RT-PCR with primers located in exon 21 and 23. Diagrams on the right show the structures of STAT3 pre-mRNA and spliced products. Short lines above or below exons stand for primer positions. An exon 22/23 backward junction primer was used to specifically amplify short product, STAT3β. (E) Overexpression of exogenous T7 tagged PCBP1 was confirmed by western blot. LV: lentivirus. GAPDH served as a loading control. (F-G) Alternative splicing of STAT3 and the expression of PCBP1 in normal and oral cancer cells were analyzed by RT-PCR or western blot.