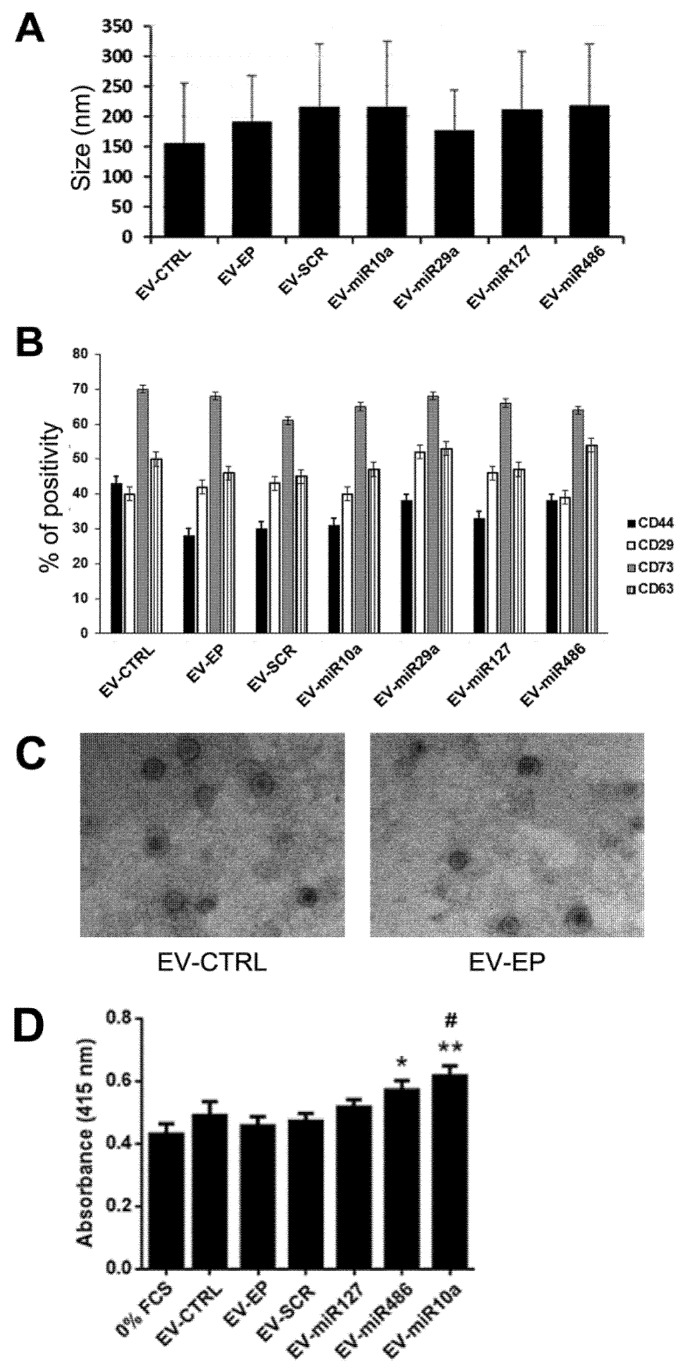
Figure 4.
Characterization of EVs derived from naïve MSCs and from EP MSCs. (A) Size of EVs obtained from naïve MSC (EV-CTRL), from electroporated MSC (EV-EP) and transfected with scramble (EV-SCR) or with different miRNA mimics (EV-mir10a, EV-miR29a, EV-miR127, EV-miR486), evaluated by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). Data reported are mean ± SD for three different experiments. No statistically significant differences were observed among the different types of EVs; (B) cytofluorimetric analysis of the expression of MSC (CD44, CD29 and CD73) and exosomal (CD63) markers, in different EV populations. Data reported are the mean ± SD for three different experiments. No statistically significant differences were observed in marker expression among the different types of EVs; (C) representative micrographs of transmission electron microscopy of EV-CTRL (left) and EV-EP (right). EVs negatively stained with NanoVan (magnification ×100,000); and (D) different types of EVs (1000/cells) were added to mTECs maintained for 48 h in hypoxia, after which proliferation was evaluated following 24 h of reoxygenation. Data are reported as mean ± SEM for three different experiments in quadruplicate. ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test was performed. ** p < 0.01 and * p < 0.05 mTEC stimulated with EV-mimic vs. mTEC maintained in 0% FCS, # p < 0.05 EV-miR10a vs. mTEC stimulated with EV-EP.