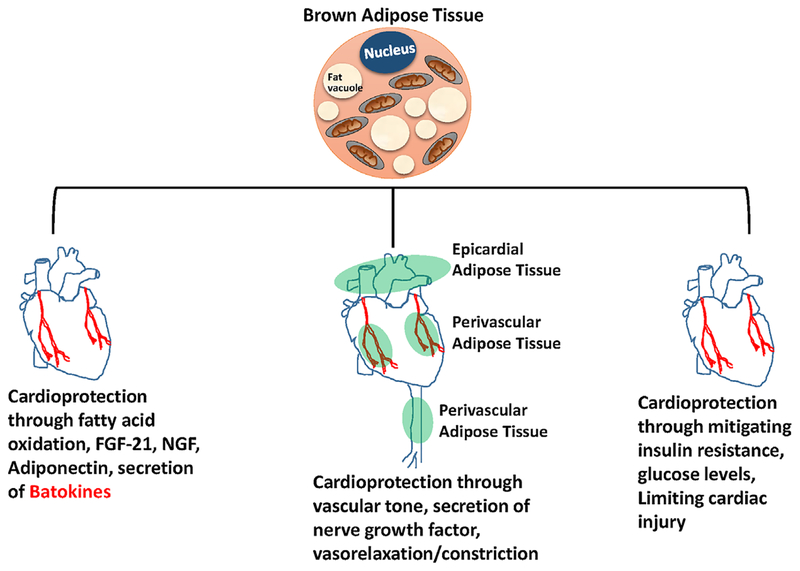
Fig. 3.
Cardioprotection through browning of fat. Browning of fat can lead to cardioprotection in three ways: (I) by secreting batokines like FGF2I, adiponectin, nerve growth factors, and free fatty acids; (2) by maintaining vascular tone through secretion of vasorelaxing/vasoconstricting factors from perivascular and epicardial tissues; and (3) by reducing the levels of triglycerides and mitigating insulin resistance and limiting cardiac injury.