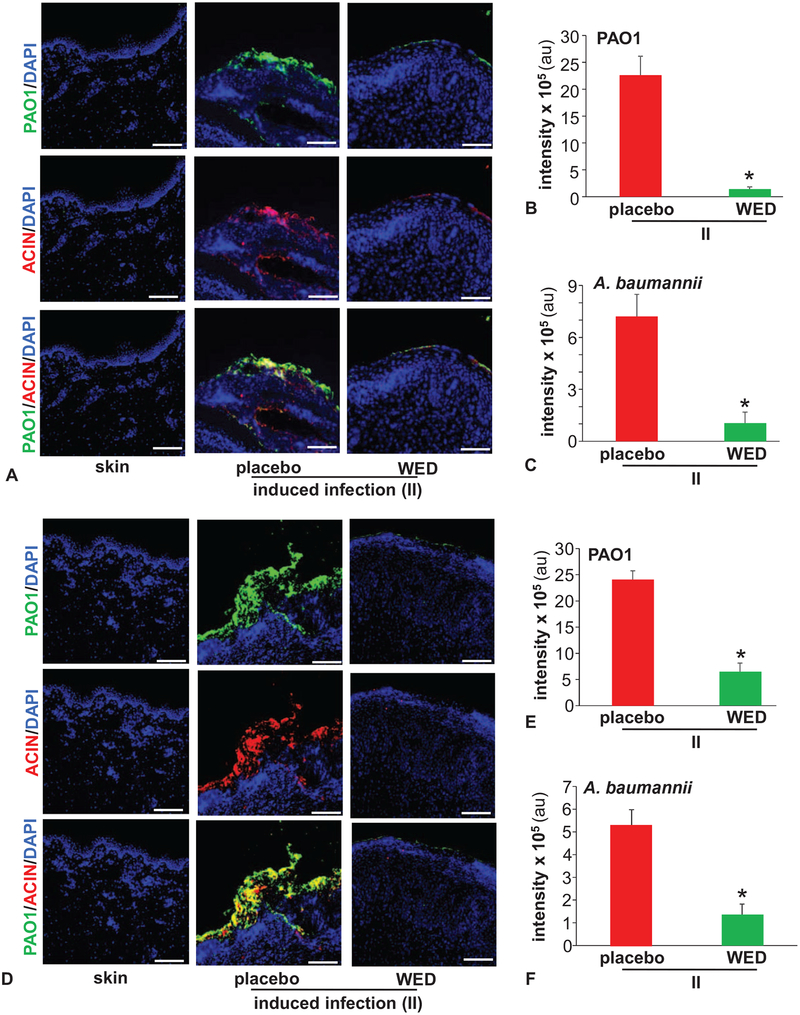
FIGURE 1.
WED disrupted bacterial aggregates on the wound surface. Porcine burn wounds (2 × 2 sq inch) were subjected to induced infection (II) on day 3 post-burn with P. aeruginosa PAO1 and A. baumannii 19606. The burn wounds were treated with WED either 2 h post-inoculation to study “prevention” or 7 days post-inoculation to evaluate the “rescue” efficacy of WED against biofilm infection. The WED dressing was changed twice a week throughout the duration of the study. Representative immunofluorescence images of day 56 post-inoculation burn wound biopsies in A–C, prevention or D–F, rescue studies. P. aeruginosa and A. baumannii were visualized using anti-Pseudomonas (green) or anti-Acinetobacter (red) antibody. Quantifications represent intensity of individual stains. Scale bar = 100 μm. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3–5), *P < 0.05 compared with placebo (Student t test, 2-tailed).