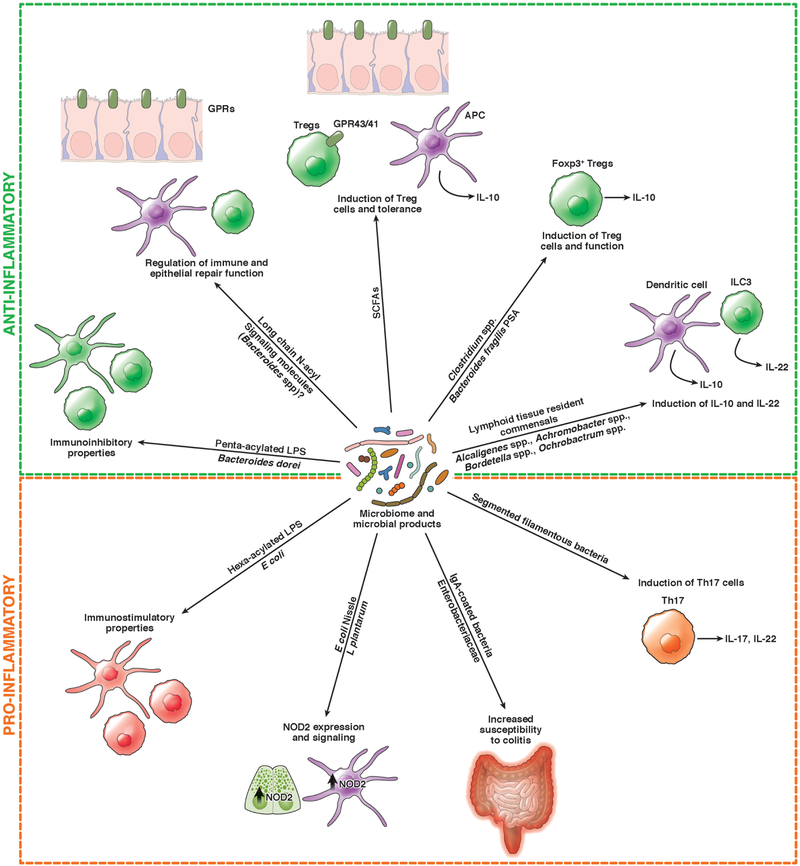
Figure 2. Effects of the Microbiome on Intestinal and Immune Cells.
The intestinal microbiome and its products modulate immune responses, via induction of dendritic cells (DCs) and lymphocytes (such as Th17 cells, Treg cells [Tregs in figure], and innate lymphoid cells (ILCs)), and cytokine production (IL10, IL22). Intestinal bacteria can also modulate immune signaling pathways, such as expression of NOD2, and epithelial repair. Specific microbes can increase susceptibility of mice to colitis.