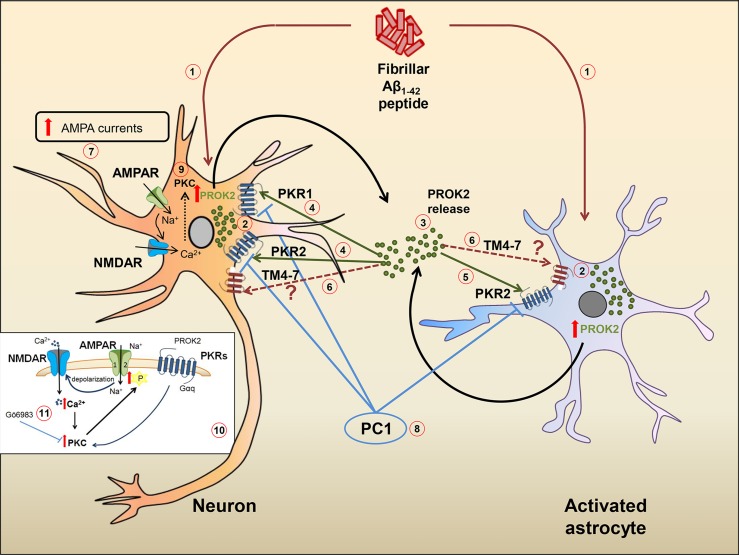
Figure 1.
Hypothetical role of the PK system in Aβ-mediated cell toxicity. Ab1−42 peptide (1) induces an increase of PROK2 in both neurons and astrocytes (2). Once released (3), PROK2 binds to PKR1 and PKR2 on neurons (4) and on PKR2 localized on astrocytes (5). PROK2 may also bind to the PKR2-truncated isoform (TM4-7) whose cell type localization and function is still unknown (6). At neuronal level, the increase of AMPA-receptor ionic currents induced by Aβ (but also by Bv8) (7) seems to be mediated by the PK system, as it is blocked by the PKR antagonist PC1 (8). The up-modulation of AMPA ionic currents may be mediated by the activation of PKC intracellular pathways (9) [in detail illustrated in the small box (10)], as confirmed by the antagonistic effect of PKC inhibitor Go6983 (11).